Platform S5 Enable Guide¶
Introduction¶
S5 is one of the ACPI sleep states that refers to the system being shut down (although some power may still be supplied to certain devices). In this document, S5 means the function to shut down the User VMs, the Service VM, the hypervisor, and the hardware. In most cases, directly shutting down the power of a computer system is not advisable because it can damage some components. It can cause corruption and put the system in an unknown or unstable state. On ACRN, the User VM must be shut down before powering off the Service VM. Especially for some use cases, where User VMs could be used in industrial control or other high safety requirement environment, a graceful system shutdown such as the ACRN S5 function is required.
S5 Architecture¶
ACRN provides a mechanism to trigger the S5 state transition throughout the system. It uses a vUART channel to communicate between the Service and User VMs. The diagram below shows the overall architecture:
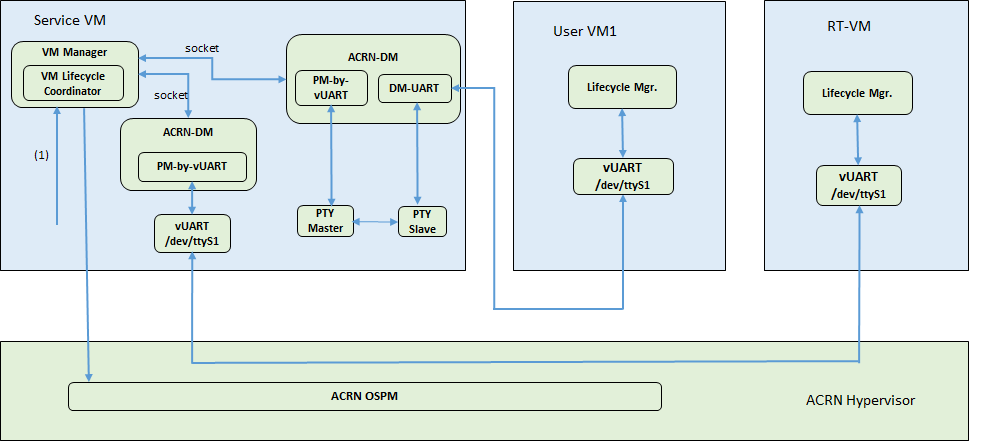
Figure 77 S5 overall architecture
Scenario I:
The User VM’s serial port device (
ttySn) is emulated in the Device Model, the channel from the Service VM to the User VM:![digraph G {
node [shape=plaintext fontsize=12];
graph [rankdir=LR];
subgraph cluster_0 {
node [shape=box];
label="PTY"
"Master" -> "Slave" [dir=both arrowsize=.5];
}
"ACRN-DM" -> "Master" [arrowsize=.5];
"Slave" -> "User VM:/dev/ttyS1" [arrowsize=.5];
}](../_images/graphviz-58d84c621a0a35bd460226fc5370c4d8c8813666.png)
Scenario II:
The User VM’s (like RT-Linux or other RT-VMs) serial port device (
ttySn) is emulated in the Hypervisor, the channel from the Service OS to the User VM:![digraph G {
node [shape=plaintext fontsize=12];
rankdir=LR;
bgcolor="transparent";
"ACRN-DM" -> "Service VM:/dev/ttyS1" -> "ACRN hypervisor" -> "User VM:/dev/ttyS1" [arrowsize=.5];
}](../_images/graphviz-d2e6244261a2fdcf55b89138b243387499805ab4.png)
Trigger the User VM’s S5¶
On the Service VM side, it uses the acrnctl tool to trigger the User VM’s S5 flow:
acrnctl stop user-vm-name. Then, the Device Model sends a shutdown command
to the User VM through a channel. If the User VM receives the command, it will send an “ACK”
to the Device Model. It is the Service VM’s responsibility to check if the User VMs
shutdown successfully or not, and decides when to power off itself.
User VM “life-cycle manager”¶
As part of the current S5 reference design, a life-cycle manager daemon (life_mngr) runs in the
User VM to implement S5. It waits for the command from the Service VM on the
paired serial port. The simple protocol between the Service VM and User VM is as follows:
When the daemon receives shutdown, it sends “acked” to the Service VM;
then it can power off the User VM. If the User VM is not ready to power off,
it can ignore the shutdown command.
Enable S5¶
The procedure for enabling S5 is specific to the particular OS:
For Linux (LaaG) or Windows (WaaG), refer to the following configurations in the
devicemodel/samples/nuc/launch_uos.shlaunch script foracrn-dm.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
#for pm by vuart setting pm_channel="--pm_notify_channel uart " pm_by_vuart="--pm_by_vuart pty,/run/acrn/life_mngr_"$vm_name pm_vuart_node=" -s 1:0,lpc -l com2,/run/acrn/life_mngr_"$vm_name #for memsize setting mem_size=2048M acrn-dm -A -m $mem_size -s 0:0,hostbridge \ -s 2,pci-gvt -G "$2" \ -s 5,virtio-console,@stdio:stdio_port \ -s 6,virtio-hyper_dmabuf \ -s 3,virtio-blk,/home/clear/uos/uos.img \ -s 4,virtio-net,tap0 \ -s 7,virtio-rnd \ --ovmf /usr/share/acrn/bios/OVMF.fd \ $pm_channel $pm_by_vuart $pm_vuart_node \ $logger_setting \ --mac_seed $mac_seed \ $vm_name }
For RT-Linux, refer to the
devicemodel/samples/nuc/launch_hard_rt_vm.shscript:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
# for pm setting pm_channel="--pm_notify_channel uart " pm_by_vuart="--pm_by_vuart tty,/dev/ttyS1" /usr/bin/acrn-dm -A -m $mem_size -s 0:0,hostbridge \ --lapic_pt \ --rtvm \ --virtio_poll 1000000 \ -U 495ae2e5-2603-4d64-af76-d4bc5a8ec0e5 \ -s 2,passthru,02/0/0 \ -s 3,virtio-console,@stdio:stdio_port \ $pm_channel $pm_by_vuart \ --ovmf /usr/share/acrn/bios/OVMF.fd \ hard_rtvm }
Note
For RT-Linux, the vUART is emulated in the hypervisor; expose the node as
/dev/ttySn.
For LaaG and RT-Linux VMs, run the life-cycle manager deamon:
Use these commands to build the life-cycle manager daemon,
life_mngr.$ cd acrn-hypervisor/misc/life_mngr $ make life_mngr
Copy
life_mngrandlife_mngr.serviceinto the User VM:$ scp life_mngr root@<test board address>:/usr/bin/life_mngr $ scp life_mngr.service root@<test board address>:/lib/systemd/system/life_mngr.service
Use the below commands to enable
life_mngr.serviceand restart the User VM.# chmod +x /usr/bin/life_mngr # systemctl enable life_mngr.service # reboot
For the WaaG VM, run the life-cycle manager deamon:
Build the
life_mngr_win.exeapplication:$ cd acrn-hypervisor/misc $ make life_mngr
Note
If there is no
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcccompiler, you must runswupd bundle-add c-basic-mingwto install it.Set up a Windows environment:
Download the Visual Studio 2019 tool from https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/, and choose the two options in the below screenshots to install “Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2015, 2017 and 2019 (x86 or X64)” in WaaG:
In WaaG, use the WIN + R shortcut key, input “shell:startup”, click OK and then copy the
life_mngr_win.exeapplication into this directory.
Restart the WaaG VM. The COM2 window will automatically open after reboot.
If the Service VM is being shut down (transitioning to the S5 state), it can call
acrnctl stop vm-nameto shut down the User VMs.Note
S5 state is not automatically triggered by a Service VM shutdown; this needs to be run before powering off the Service VM.
How to test¶
Note
The CBC tools and service installed by the software-defined-cockpit bundle will conflict with the vUART and hence need to be masked.
systemctl mask cbc_attach
systemctl mask cbc_thermal_fuse
systemctl mask cbc_thermald
systemctl mask cbc_lifecycle.service
Or:
ps -ef|grep cbc; kill -9 cbc_pid
Refer to the Enable S5 section to set up the S5 environment for the User VMs.
Note
RT-Linux’s UUID must use
495ae2e5-2603-4d64-af76-d4bc5a8ec0e5. Also, the industry EFI image is required for launching the RT-Linux VM.Note
Use the
systemctl status life_mngr.servicecommand to ensure the service is working on the LaaG or RT-Linux:● life_mngr.service - ACRN lifemngr daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/life_mngr.service; enabled; vendor p> Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-09-10 07:15:06 UTC; 1min 11s ago Main PID: 840 (life_mngr)
Note
For WaaG, we need to close
windbgby using the"bcdedit /set debug offcommand IF you executed thebcdedit /set debug onwhen you set up the WaaG, because it occupies theCOM2.Use the``acrnctl stop`` command on the Service VM to trigger S5 to the User VMs:
# acrnctl stop vm1Use the
acrnctl listcommand to check the User VM status.# acrnctl list vm1 stopped