ACRN v2.0 (Jun 2020)¶
We are pleased to announce the second major release of the Project ACRN hypervisor.
ACRN v2.0 offers new and improved scenario definitions, with a focus on industrial IoT and edge device use cases. ACRN supports these uses with their demanding and varying workloads including Functional Safety certification, real-time characteristics, device and CPU sharing, and general computing power needs, while honoring required isolation and resource partitioning. A wide range of User VM OSs (such as Windows 10, Ubuntu, Android, and VxWorks) can run on ACRN, running different workloads and applications on the same hardware platform.
A new hybrid-mode architecture adds flexibility to simultaneously support both traditional resource sharing among VMs and complete VM resource partitioning required for functional safety requirements.
Workload management and orchestration, rather standard and mature in cloud environments, are enabled now in ACRN, allowing open source orchestrators such as OpenStack to manage ACRN virtual machines. Kata Containers, a secure container runtime, has also been enabled on ACRN and can be orchestrated via Docker or Kubernetes.
Rounding things out, we’ve also made significant improvements in configuration tools, added many new tutorial documents, and enabled ACRN on the QEMU machine emulator making it easier to try out and develop with ACRN.
ACRN is a flexible, lightweight reference hypervisor that is built with real-time and safety-criticality in mind. It is optimized to streamline embedded development through an open source platform. Check out What Is ACRN for more information. All project ACRN source code is maintained in the https://github.com/projectacrn/acrn-hypervisor repository and includes folders for the ACRN hypervisor, the ACRN device model, tools, and documentation. You can either download this source code as a zip or tar.gz file (see the ACRN v2.0 GitHub release page) or use Git clone and checkout commands:
git clone https://github.com/projectacrn/acrn-hypervisor
cd acrn-hypervisor
git checkout v2.0
The project’s online technical documentation is also tagged to correspond with a specific release: generated v2.0 documents can be found at https://projectacrn.github.io/2.0/. Documentation for the latest (master) branch is found at https://projectacrn.github.io/latest/. Follow the instructions in the Getting Started Guide to get started with ACRN.
We recommend that all developers upgrade to ACRN release v2.0.
Version 2.0 Key Features (Comparing With v1.0)¶
ACRN Architecture Upgrade to Support Hybrid Mode¶
The ACRN architecture has evolved after its initial major 1.0 release in May 2019. The new hybrid mode architecture has the flexibility to support both partition mode and sharing mode simultaneously, as shown in this architecture diagram:
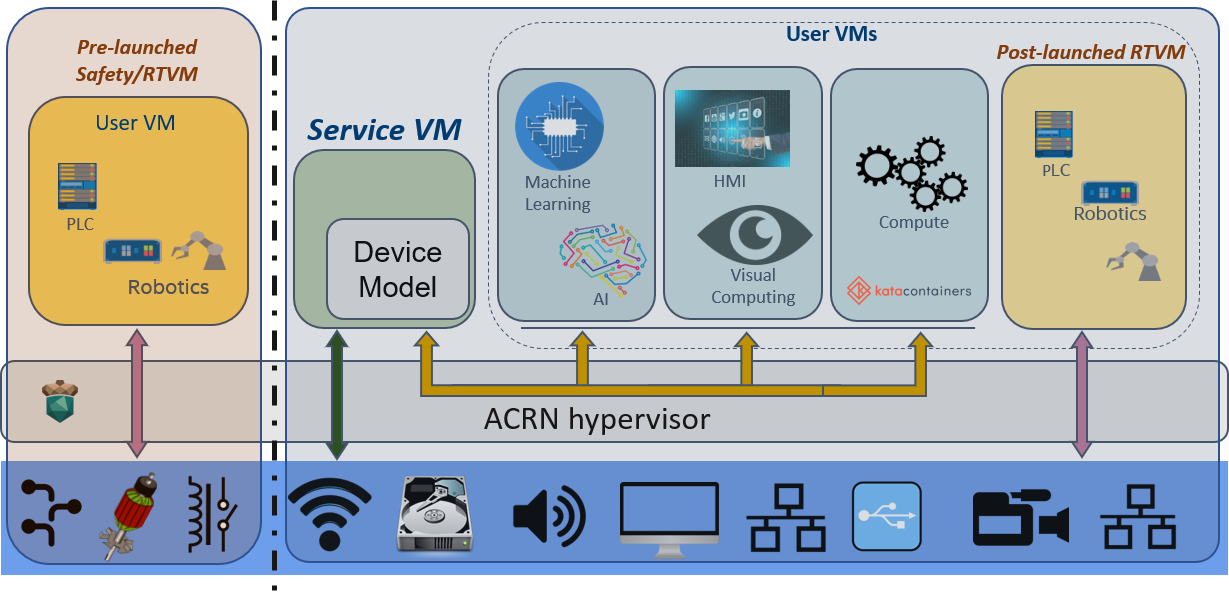
Figure 245 ACRN V2 high-level architecture¶
On the left, resources are partitioned and used by a pre-launched User Virtual Machine (VM), started by the hypervisor before the Service VM has been launched. It runs independent of other virtual machines, and can own its own dedicated hardware resources, such as a CPU core, memory, and I/O devices. Because other VMs may not even be aware of its existence, this pre-launched VM can be used as a safety VM where, for example, platform hardware failure detection code can run and take emergency actions if a system critical failure occurs.
On the right, the remaining hardware resources are shared by the Service VM and User VMs. The Service VM can access hardware resources directly (by running native drivers) and offer device sharing services to other User VMs by the Device Model.
Also on the right, a special post-launched real-time VM (RTVM) can run a hard real-time OS, such as VxWorks*, Zephyr*, or Xenomai*. Because of its real-time capabilities, the RTVM can be used for soft PLC, IPC, or Robotics applications.
New Hardware Platform Support¶
This release adds support for 8th Gen Intel® Core™ Processors (code name: Whiskey Lake). (See Supported Hardware for platform details.)
Pre-Launched Safety VM Support¶
ACRN supports a pre-launched partitioned safety VM, isolated from the Service VM and other post-launched VM by using partitioned HW resources. For example, in the hybrid mode, a real-time Zephyr RTOS VM can be pre-launched by the hypervisor even before the Service VM is launched, and with its own dedicated resources to achieve a high level of isolation. This is designed to meet the needs of a Functional Safety OS.
Post-Launched VM Support via OVMF¶
ACRN supports Open Virtual Machine Firmware (OVMF) as a virtual boot loader for the Service VM to launch post-launched VMs such as Windows, Linux, VxWorks, or Zephyr RTOS. Secure boot is also supported.
Post-Launched Real-Time VM Support¶
ACRN supports a post-launched RTVM, which also uses partitioned hardware resources to ensure adequate real-time performance, as required for industrial use cases.
Real-Time VM Performance Optimizations¶
ACRN 2.0 improves RTVM performance with these optimizations:
- Eliminate use of VM-Exit and its performance overhead:
Use Local APIC (LAPIC) passthrough, Virtio Polling Mode Drivers (PMD), and NMI interrupt notification technologies.
- Isolate the RTVM from the Service VM:
The ACRN hypervisor uses RDT (Resource Director Technology) allocation features such as CAT (Cache Allocation Technology), CDP (Code Data Prioritization), and MBA (Memory Bandwidth Allocation) to provide better isolation and prioritize critical resources, such as cache and memory bandwidth, for RTVMs over other VMs.
- PCI Configuration space access emulation for passthrough devices in the hypervisor:
The hypervisor provides the necessary emulation (such as config space) of the passthrough PCI device during runtime for a DM-launched VM from Service VM.
- More hypervisor-emulated devices:
This includes vPCI and vPCI bridge emulation, and vUART.
- ART (Always Running Timer Virtualization):
Ensure time is synchronized between Ptdev and vART
CPU Sharing Support¶
ACRN supports CPU Sharing to fully utilize the physical CPU resource across more virtual machines. ACRN enables a borrowed virtual time CPU scheduler in the hypervisor to make sure the physical CPU can be shared between VMs and support for yielding an idle vCPU when it’s running a ‘HLT’ or ‘PAUSE’ instruction.
Large Selection of OSs for User VMs¶
ACRN now supports Windows* 10, Android*, Ubuntu*, Xenomai, VxWorks*, real-time Linux*, and Zephyr* RTOS. ACRN’s Windows support now conforms to the Microsoft* Hypervisor Top-Level Functional Specification (TLFS). ACRN 2.0 also improves overall Windows as a Guest (WaaG) stability and performance.
GRUB Bootloader¶
The ACRN hypervisor can boot from the popular GRUB bootloader using either the multiboot or multiboot2 prococol (the latter adding UEFI support). GRUB provides developers with booting flexibility.
SR-IOV Support¶
SR-IOV (Single Root Input/Output Virtualization) can isolate PCIe devices to offer performance similar to bare-metal levels. For a network adapter, for example, this enables network traffic to bypass the software switch layer in the virtualization stack and achieve network performance that is nearly the same as in a nonvirtualized environment. In this example, the ACRN Service VM supports a SR-IOV ethernet device through the Physical Function (PF) driver, and ensures that the SR-IOV Virtual Function (VF) device can passthrough to a post-launched VM.
Graphics Passthrough Support¶
ACRN supports GPU passthrough to dedicated User VM based on Intel GVT-d technology used to virtualize the GPU for multiple guest VMs, effectively providing near-native graphics performance in the VM.
Configuration Tool Support¶
A new offline configuration tool helps developers deploy ACRN to different hardware systems with its own customization.
Kata Containers Support¶
ACRN can launch a Kata container, a secure container runtime, as a User VM.
VM Orchestration¶
Libvirt is an open-source API, daemon, and management tool as a layer to decouple orchestrators and hypervisors. By adding a “ACRN driver”, ACRN supports libvirt-based tools and orchestrators to configure a User VM’s CPU configuration during VM creation.
Document Updates¶
Many new and updated reference documents are available, including:
General
Getting Started
Configuration and Tools
Service VM Tutorials
User VM Tutorials
Enable ACRN Features
Enable OVS in ACRN
Enable QoS based on runC Containers
Debug
High-Level Design Guides
Fixed Issues Details¶
3715 - Add support for multiple RDT resource allocation and fix L3 CAT config overwrite by L2
3770 - Warning when building the ACRN hypervisor `SDC (defined at arch/x86/Kconfig:7) set more than once`
3773 - suspicious logic in vhost.c
3918 - Change active_hp_work position for code cleaning and add a module parameter to disable hp work.
3939 - zero-copy non-functional with vhost
3946 - Cannot boot VxWorks as UOS on KabyLake
4017 - hv: rename vuart operations
4046 - Error info popoup when run 3DMARK11 on Waag
4072 - hv: add printf “not support the value of vuart index parameter” in function vuart_register_io_handler
4191 - acrnboot: the end address of _DYNAME region is not calculated correct
4250 - acrnboot: parse hv cmdline incorrectly when containing any trailing white-spaces
4283 - devicemodel: refactor CMD_OPT_LAPIC_PT case branch
4314 - RTVM boot up fail due to init_hugetlb failed during S5 testing
4365 - Enable GOP driver work in GVT-d scenario
4520 - efi-stub could get wrong bootloader name
4628 - HV: guest: fix bug in get_vcpu_paging_mode
4630 - The `board_parser.py` tool contains a few grammatical mistakes and typos
4664 - Wake up vCPU for interrupts from vPIC
4666 - Fix offline tool to generate info in pci_dev file for logical partition scenario
4680 - Fix potential dead loop if VT-d QI request timeout
4688 - RELEASE=n does not take effect while using xml to make hypervisor
4703 - Failed to launch WaaG at a high probablity if enable CPU sharing in GVT-d.
4711 - WaaG reboot will core dump with USB mediator
4797 - [acrn-configuration-tool] The VM name is always 1 when using web app to generate the launch script
4799 - [acrn-configuration-tool]wrong parameter for Soft RT/Hard RT vm in launch script
4827 - Missing explicit initialization of pci_device_lock
4868 - [acrn-configuation-tool]efi bootloader image file of Yocto industry build not match with default xmls
4889 - [WHL][QEMU][HV] With latest master branch HV, build ACRN for Qemu fail
Known Issues¶
4047 - [WHL][Function][WaaG] passthru usb, Windows will hang when reboot it
4313 - [WHL][VxWorks] Failed to ping when VxWorks passthru network
4557 - [WHL][Performance][WaaG] Failed to run 3D directX9 during Passmark9.0 performance test with 7212 gfx driver
4558 - [WHL][Performance][WaaG] WaaG reboot automatically during run 3D directX12 with 7212 gfx driver
4982 - [WHL]ivshmemTest transfer file failed after UOS shutdown or reboot
4983 - [WHL][RTVM]without any virtio device, with only pass-through devices, RTVM can’t boot from SATA