I/O Emulation High-Level Design¶
As discussed in Device Emulation, there are multiple ways and places to handle I/O emulation, including HV, Service VM Kernel HSM, and Service VM user-land Device Model (acrn-dm).
I/O emulation in the hypervisor provides these functionalities:
Maintain lists of port I/O or MMIO handlers in the hypervisor for emulating trapped I/O accesses in a certain range.
Forward I/O accesses to Service VM when they cannot be handled by the hypervisor by any registered handlers.
Figure 102 illustrates the main control flow steps of I/O emulation inside the hypervisor:
Trap and decode I/O access by VM exits and decode the access from exit qualification or by invoking the instruction decoder.
If the range of the I/O access overlaps with any registered handler, call that handler if it completely covers the range of the access, or ignore the access if the access crosses the boundary.
If the range of the I/O access does not overlap the range of any I/O handler, deliver an I/O request to Service VM.
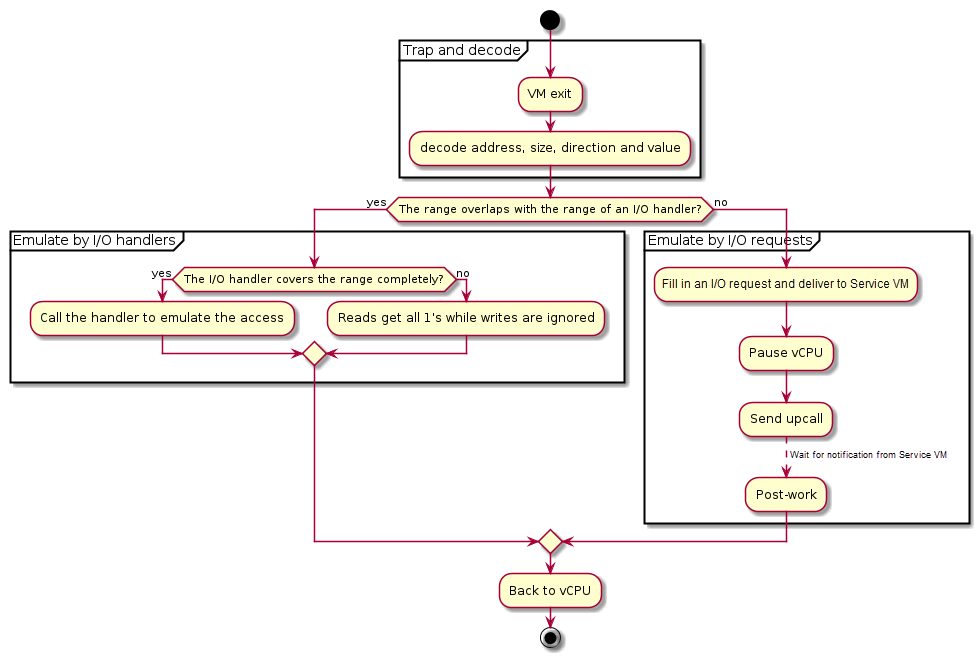
Figure 102 Control Flow of I/O Emulation in the Hypervisor¶
I/O emulation does not rely on any calibration data.
Trap Path¶
Port I/O accesses are trapped by VM exits with the basic exit reason “I/O instruction”. The port address to be accessed, size, and direction (read or write) are fetched from the VM exit qualification. For writes the value to be written to the I/O port is fetched from guest registers al, ax or eax, depending on the access size.
MMIO accesses are trapped by VM exits with the basic exit reason “EPT violation”. The instruction emulator is invoked to decode the instruction that triggers the VM exit to get the memory address being accessed, size, direction (read or write), and the involved register.
The I/O bitmaps and EPT are used to configure the addresses that will trigger VM exits when accessed by a VM. Refer to IO/MMIO Emulation for details.
I/O Emulation in the Hypervisor¶
When a port I/O or MMIO access is trapped, the hypervisor first checks whether the to-be-accessed address falls in the range of any registered handler, and calls the handler when such a handler exists.
Handler Management¶
Each VM has two lists of I/O handlers, one for port I/O and the other for MMIO. Each element of the list contains a memory range and a pointer to the handler which emulates the accesses falling in the range. See Initialization and Deinitialization for descriptions of the related data structures.
The I/O handlers are registered on VM creation and never changed until the destruction of that VM, when the handlers are unregistered. If multiple handlers are registered for the same address, the one registered later wins. See Initialization and Deinitialization for the interfaces used to register and unregister I/O handlers.
I/O Dispatching¶
When a port I/O or MMIO access is trapped, the hypervisor first walks through the corresponding I/O handler list in the reverse order of registration, looking for a proper handler to emulate the access. The following cases exist:
If a handler whose range overlaps the range of the I/O access is found,
If the range of the I/O access falls completely in the range the handler can emulate, that handler is called.
Otherwise it is implied that the access crosses the boundary of multiple devices which the hypervisor does not emulate. Thus no handler is called and no I/O request will be delivered to Service VM. I/O reads get all 1’s and I/O writes are dropped.
If the range of the I/O access does not overlap with any range of the handlers, the I/O access is delivered to Service VM as an I/O request for further processing.
I/O Requests¶
An I/O request is delivered to Service VM vCPU 0 if the hypervisor does not find any handler that overlaps the range of a trapped I/O access. This section describes the initialization of the I/O request mechanism and how an I/O access is emulated via I/O requests in the hypervisor.
Initialization¶
For each User VM the hypervisor shares a page with Service VM to exchange I/O requests. The 4-KByte page consists of 16 256-Byte slots, indexed by vCPU ID. It is required for the DM to allocate and set up the request buffer on VM creation, otherwise I/O accesses from User VM cannot be emulated by Service VM, and all I/O accesses not handled by the I/O handlers in the hypervisor will be dropped (reads get all 1’s).
Refer to the following sections for details on I/O requests and the initialization of the I/O request buffer.
Types of I/O Requests¶
There are four types of I/O requests:
I/O Request Type |
Description |
|---|---|
PIO |
A port I/O access. |
MMIO |
A MMIO access to a GPA with no mapping in EPT. |
PCI |
A PCI configuration space access. |
WP |
A MMIO access to a GPA with a read-only mapping in EPT. |
For port I/O accesses, the hypervisor will always deliver an I/O request of type PIO to Service VM. For MMIO accesses, the hypervisor will deliver an I/O request of either MMIO or WP, depending on the mapping of the accessed address (in GPA) in the EPT of the vCPU. The hypervisor will never deliver any I/O request of type PCI, but will handle such I/O requests in the same ways as port I/O accesses on their completion.
Refer to Data Structures and Interfaces for a detailed description of the data held by each type of I/O request.
I/O Request State Transitions¶
Each slot in the I/O request buffer is managed by a finite state machine with four states. The following figure illustrates the state transitions and the events that trigger them.
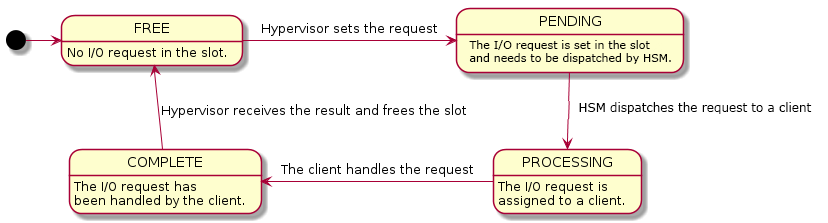
Figure 103 State Transition of I/O Requests¶
The four states are:
- FREE
The I/O request slot is not used and new I/O requests can be delivered. This is the initial state on User VM creation.
- PENDING
The I/O request slot is occupied with an I/O request pending to be processed by Service VM.
- PROCESSING
The I/O request has been dispatched to a client but the client has not finished handling it yet.
- COMPLETE
The client has completed the I/O request but the hypervisor has not consumed the results yet.
The contents of an I/O request slot are owned by the hypervisor when the state of an I/O request slot is FREE or COMPLETE. In such cases Service VM can only access the state of that slot. Similarly the contents are owned by Service VM when the state is PENDING or PROCESSING, when the hypervisor can only access the state of that slot.
The states are transferred as follow:
To deliver an I/O request, the hypervisor takes the slot corresponding to the vCPU triggering the I/O access, fills the contents, changes the state to PENDING and notifies Service VM via upcall.
On upcalls, Service VM dispatches each I/O request in the PENDING state to clients and changes the state to PROCESSING.
The client assigned an I/O request changes the state to COMPLETE after it completes the emulation of the I/O request. A hypercall is made to notify the hypervisor on I/O request completion after the state change.
The hypervisor finishes the post-work of a I/O request after it is notified on its completion and change the state back to FREE.
States are accessed using atomic operations to avoid getting unexpected states on one core when it is written on another.
Note that there is no state to represent a ‘failed’ I/O request. Service VM should return all 1’s for reads and ignore writes whenever it cannot handle the I/O request, and change the state of the request to COMPLETE.
Post-Work¶
After an I/O request is completed, some more work needs to be done for I/O reads to update guest registers accordingly. The hypervisor re-enters the vCPU thread every time a vCPU is scheduled back in, rather than switching to where the vCPU is scheduled out. As a result, post-work is introduced for this purpose.
The hypervisor pauses a vCPU before an I/O request is delivered to Service VM. Once the I/O request emulation is completed, a client notifies the hypervisor by a hypercall. The hypervisor will pick up that request, do the post-work, and resume the guest vCPU. The post-work takes care of updating the vCPU guest state to reflect the effect of the I/O reads.
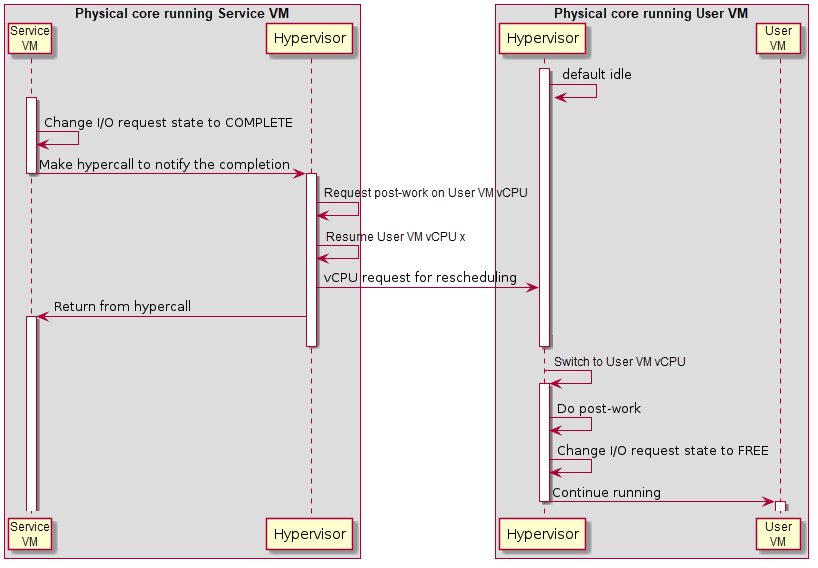
Figure 104 Workflow of MMIO I/O Request Completion¶
The figure above illustrates the workflow to complete an I/O request for MMIO. Once the I/O request is completed, Service VM makes a hypercall to notify the hypervisor which resumes the User VM vCPU triggering the access after requesting post-work on that vCPU. After the User VM vCPU resumes, it does the post-work first to update the guest registers if the access reads an address, changes the state of the corresponding I/O request slot to FREE, and continues execution of the vCPU.
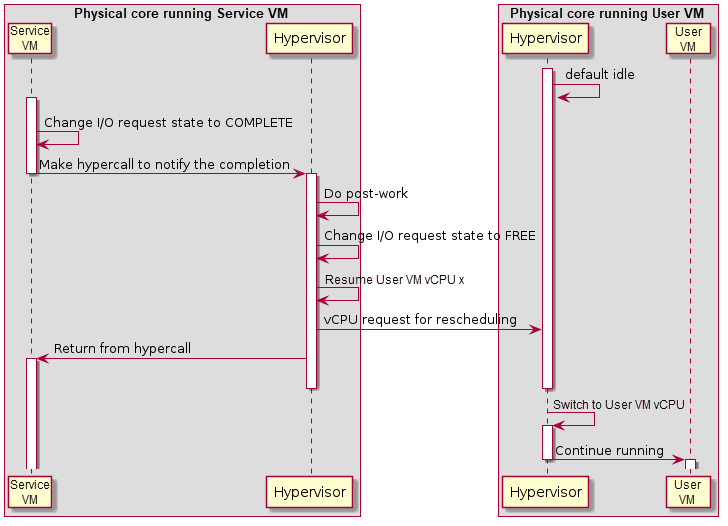
Figure 105 Workflow of Port I/O Request Completion¶
Completion of a port I/O request (shown in Figure 105 above) is similar to the MMIO case, except the post-work is done before resuming the vCPU. This is because the post-work for port I/O reads need to update the general register eax of the vCPU, while the post-work for MMIO reads need further emulation of the trapped instruction. This is much more complex and may impact the performance of the Service VM.
Data Structures and Interfaces¶
External Interfaces¶
The following structures represent an I/O request. struct acrn_io_request is the main structure and the others are detailed representations of I/O requests of different kinds.
-
struct acrn_mmio_request
Representation of a MMIO request.
-
struct acrn_pio_request
Representation of a port I/O request.
-
struct acrn_pci_request
Representation of a PCI configuration space access.
-
struct acrn_io_request
256-byte I/O requests
The state transitions of a I/O request are:
FREE -> PENDING -> PROCESSING -> COMPLETE -> FREE -> …
When a request is in COMPLETE or FREE state, the request is owned by the hypervisor. Service VM (HSM or DM) shall not read or write the internals of the request except the state.
When a request is in PENDING or PROCESSING state, the request is owned by Service VM. The hypervisor shall not read or write the request other than the state.
Based on the rules above, a typical I/O request lifecycle should looks like the following.
Service VM vCPU 0
Service VM vCPU x
User VM vCPU y
Hypervisor:
Fill in type, addr, etc.
Pause User VM vCPU
Set state to PENDING (a)
Fire upcall to Service VM vCPU 0
HSM:
Scan for pending requests
Set state to PROCESSING (b)
Assign requests to clients (c)
Client:
Scan for assigned requests
Handle the requests (d)
Set state to COMPLETE
Notify the hypervisor
Hypervisor:
resume User VM vCPU y (e)
Hypervisor:
Post-work (f)
set state to FREE
Note that the following shall hold.
(a) happens before (b)
(c) happens before (d)
(e) happens before (f)
One vCPU cannot trigger another I/O request before the previous one has completed (i.e. the state switched to FREE)
Accesses to the state of a acrn_io_request shall be atomic and proper barriers are needed to ensure that:
Setting state to PENDING is the last operation when issuing a request in the hypervisor, as the hypervisor shall not access the request any more.
Due to similar reasons, setting state to COMPLETE is the last operation of request handling in HSM or clients in Service VM.
For hypercalls related to I/O emulation, refer to I/O Emulation in the Hypervisor.
Initialization and Deinitialization¶
The following structure represents a port I/O handler:
-
struct vm_io_handler_desc¶
Describes a single IO handler description entry.
The following structure represents a MMIO handler.
-
struct mem_io_node¶
Structure for MMIO handler node.
The following APIs are provided to initialize, deinitialize or configure I/O bitmaps and register or unregister I/O handlers:
-
void allow_guest_pio_access(struct acrn_vm *vm, uint16_t port_address, uint32_t nbytes)¶
Allow a VM to access a port I/O range.
This API enables direct access from the given
vmto the port I/O space starting fromport_addresstoport_address+nbytes- 1.- Parameters
vm – The VM whose port I/O access permissions is to be changed
port_address – The start address of the port I/O range
nbytes – The size of the range, in bytes
-
void register_pio_emulation_handler(struct acrn_vm *vm, uint32_t pio_idx, const struct vm_io_range *range, io_read_fn_t io_read_fn_ptr, io_write_fn_t io_write_fn_ptr)¶
Register a port I/O handler.
- Preconditions
pio_idx < EMUL_PIO_IDX_MAX
- Parameters
vm – The VM to which the port I/O handlers are registered
pio_idx – The emulated port io index
range – The emulated port io range
io_read_fn_ptr – The handler for emulating reads from the given range
io_write_fn_ptr – The handler for emulating writes to the given range
-
void register_mmio_emulation_handler(struct acrn_vm *vm, hv_mem_io_handler_t read_write, uint64_t start, uint64_t end, void *handler_private_data, bool hold_lock)¶
Register a MMIO handler.
This API registers a MMIO handler to
vm.- Parameters
vm – The VM to which the MMIO handler is registered
read_write – The handler for emulating accesses to the given range
start – The base address of the range
read_writecan emulateend – The end of the range (exclusive)
read_writecan emulatehandler_private_data – Handler-specific data which will be passed to
read_writewhen calledhold_lock – Whether hold the lock to handle the MMIO access
- Returns
None
I/O Emulation¶
The following APIs are provided for I/O emulation at runtime:
-
int32_t acrn_insert_request(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, const struct io_request *io_req)¶
Deliver
io_reqto Service VM and suspendvcputill its completion.- Preconditions
vcpu != NULL && io_req != NULL
- Parameters
vcpu – The virtual CPU that triggers the MMIO access
io_req – The I/O request holding the details of the MMIO access
-
int32_t pio_instr_vmexit_handler(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu)¶
The handler of VM exits on I/O instructions.
- Parameters
vcpu – The virtual CPU which triggers the VM exit on I/O instruction
-
int32_t ept_violation_vmexit_handler(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu)¶
EPT violation handling.
- Parameters
vcpu – [in] the pointer that points to vcpu data structure
- Return values
-EINVAL – fail to handle the EPT violation
0 – Success to handle the EPT violation