ACRN Shell Commands¶
The ACRN hypervisor shell supports the following commands:
Command (and parameters) |
Description |
|---|---|
help |
Display information about supported hypervisor shell commands. |
version |
Display the hypervisor version information. |
vm_list |
List all VMs, displaying the VM UUID, ID, name, and state (“Started”=running). |
vcpu_list |
List all vCPUs in all VMs. |
vcpu_dumpreg <vm_id> <vcpu_id> |
Dump registers for a specific vCPU. |
dump_host_mem <hva> <length> |
Dump the host memory region as specified by the start of the region |
dump_guest_mem <vm_id> <gva> <length> |
Dump a User VM (guest) memory region based on the VM ID ( |
vm_console <vm_id> |
Switch to the VM’s console. Use Ctrl + Alt + Space to return to the ACRN shell console. |
int |
List interrupt information per CPU. |
pt |
Show passthrough device information. |
vioapic <vm_id> |
Show virtual IOAPIC (vIOAPIC) information for a specific VM. |
dump_ioapic |
Show native IOAPIC information. |
loglevel <console_loglevel> <mem_loglevel> <npk_loglevel> |
|
cpuid <leaf> [subleaf] |
Display the CPUID leaf [subleaf], in hexadecimal. |
rdmsr [-p<pcpu_id>] <msr_index> |
Read the model-specific register (MSR) at index |
wrmsr [-p<pcpu_id>] <msr_index> <value> |
Write |
vmexit [enable | disable | clear | <vm_id>] |
Controls collection and display of vmexit occurrences useful for real-time performance profiling.
|
Command Examples¶
The following sections provide further details and examples for some of these commands.
vm_list¶
The vm_list command provides the name of each virtual machine and its corresponding ID and
state.
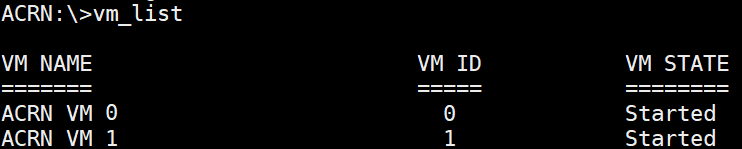
Figure 56 vm_list information¶
vcpu_list¶
The vcpu_list command provides information about virtual CPUs (vCPU), including
the VM ID, pCPU ID, vCPU ID, vCPU role (primary or secondary), and vCPU
state (init, paused, running, zombie, or unknown).
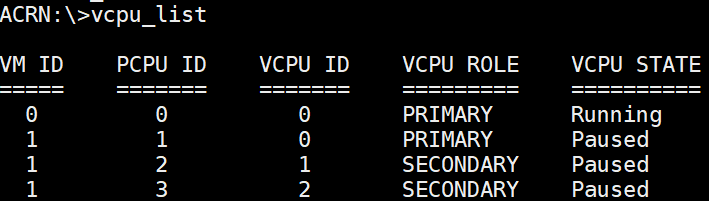
Figure 57 vcpu_list information¶
vcpu_dumpreg¶
The vcpu_dumpreg <vm_id> <vcpu_id> command provides vCPU-related
information such as register values.
In the following example, we dump the vCPU0 RIP register value and get into the Service VM to search for the running function, using these commands:
cat /proc/kallsyms | grep RIP_value
As you can see, vCPU0 is running in
function acpi_idle_do_entry.
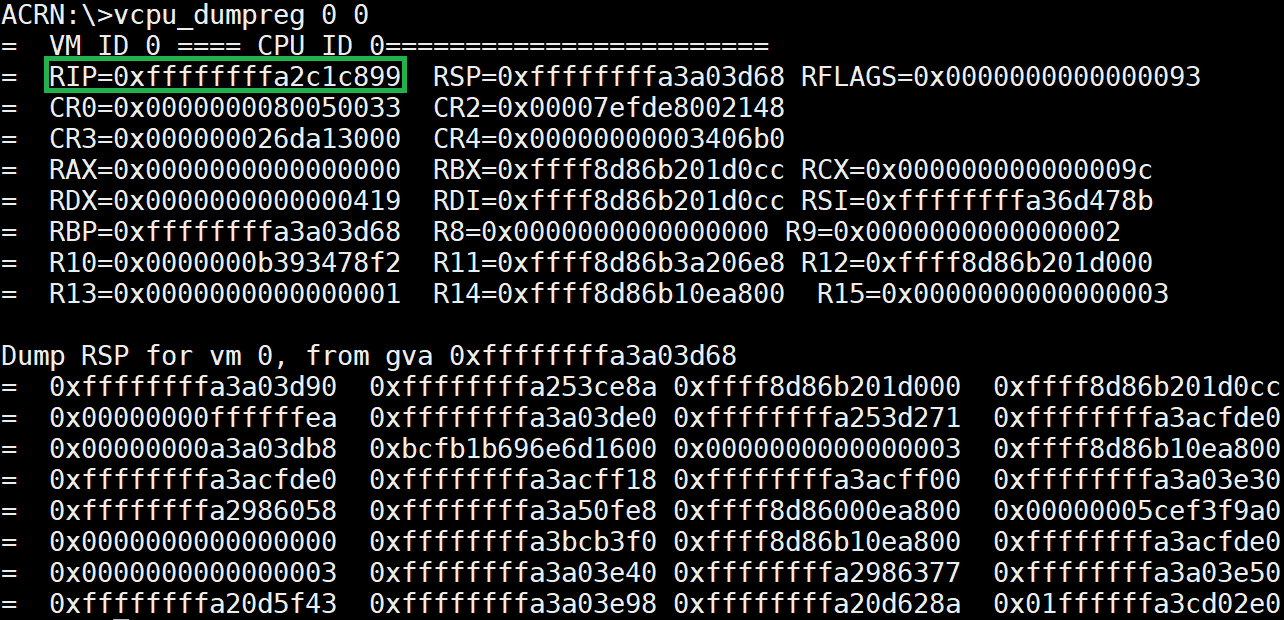
Figure 58 vcpu_dumpreg information¶
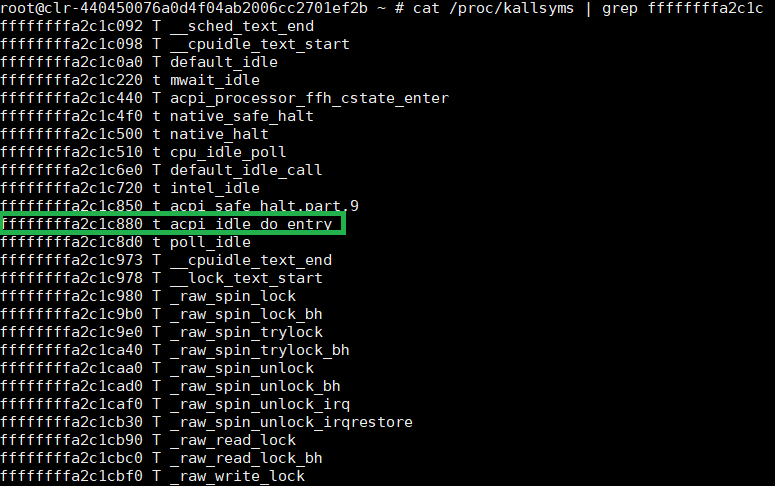
Figure 59 system map information¶
dump_host_mem¶
The dump_host_mem <hva> <length> command provides the specified memory
target data such as the physical CPU (pCPU) number.
In this example, we know the pCPU active bitmap and physical CPU number
physical memory address through
build/hypervisor/acrn.map. (Note that the path for
acrn.map depends on how we build the hypervisor.)
Then we can dump the memory address of the pCPU active bitmap and CPU number. The pCPU active bitmap is 0x000000000000000f and pCPU number is 0x0000000000000004.
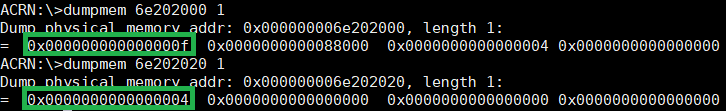
Figure 60 dumpmem information¶
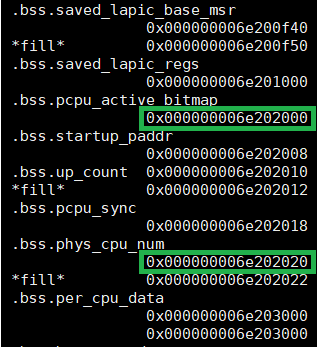
Figure 61 acrn map information¶
dump_guest_mem¶
The dump_guest_mem <vm_id> <gva> <length> command dumps guest memory
information according to the given VM ID and guest virtual address (gva).
In this example, we know the starting address of the kernel text segment
in the guest console or through the system.map. (Note that the path for
system.map depends on how we build the kernel.)

Figure 62 guest virtual address¶
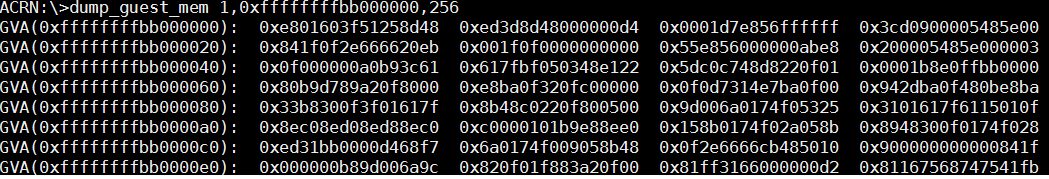
Figure 63 guest memory information¶
vm_console¶
The vm_console <vm_id> command switches the ACRN’s console to become the
VM’s console.
Press Ctrl + Alt + Space to return to the ACRN shell console.
vioapic¶
The vioapic <vm_id> command shows the virtual IOAPIC information for a specific
VM. In the following figure, we show the virtual IOAPIC information for
VM1:
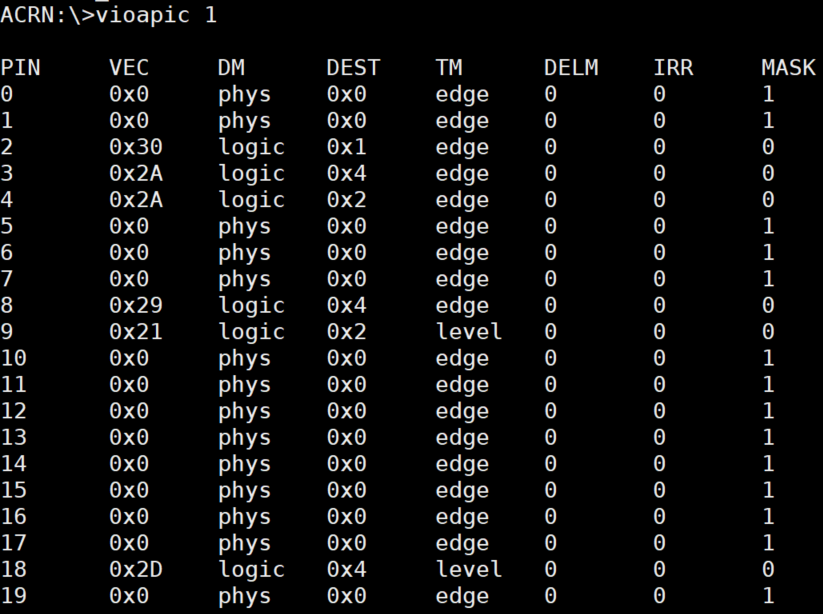
Figure 64 vioapic information¶
dump_ioapic¶
The dump_ioapic command provides IOAPIC information and we can get IRQ number,
IRQ vector number, etc.
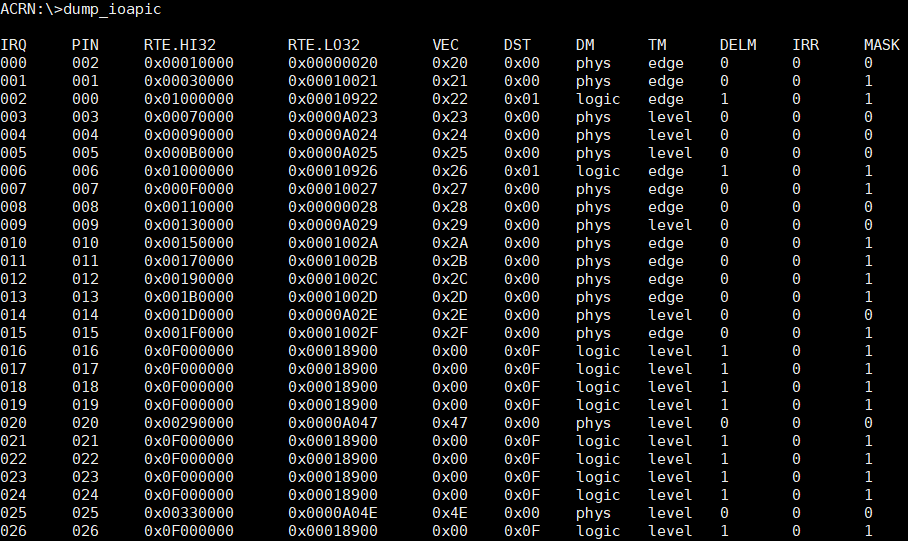
Figure 65 dump_ioapic information¶
pt¶
The pt command provides passthrough detailed information, such as the
virtual machine number, interrupt type, interrupt request, interrupt vector,
and trigger mode.
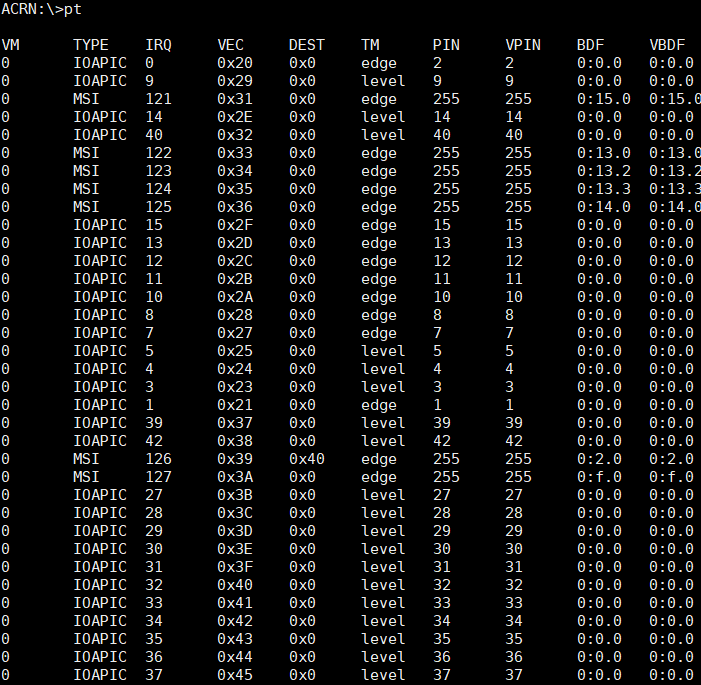
Figure 66 pt information¶
int¶
The int command provides interrupt information on all CPUs and their
corresponding interrupt vector.
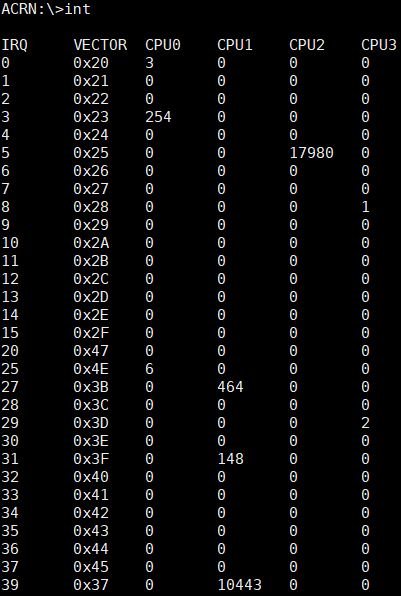
Figure 67 int information¶
cpuid¶
The cpuid <leaf> [subleaf] command provides the CPUID leaf [subleaf] in
hexadecimal.
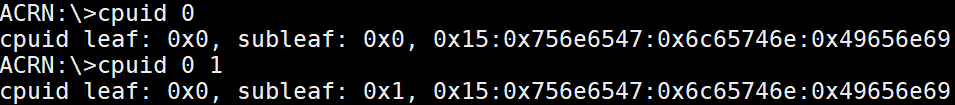
Figure 68 cpuid information¶
rdmsr¶
We can read a model-specific register (MSR) to get register
values through rdmsr [-p<pcpu_id>] <msr_index>.
In the following example, we can get the IA32_APIC_BASE value of pCPU 0 through the command:
rdmsr -p0 1b
and see that 1B (Hexadecimal) is the IA32_APIC_BASE MSR address.

Figure 69 IA32_APIC_BASE register information¶
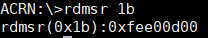
Figure 70 rdmsr information¶
wrmsr¶
We can write to a model-specific register (MSR) to set register
values through wrmsr [-p<pcpu_id>] <msr_index> <value>.
In the following example, we can set the IA32_APIC_BASE value of pCPU 1 through the command:
wrmsr -p1 1b 0xfee00c00
vmexit¶
VMexit data collection is enabled by default in a debug-mode ACRN build. There should be little impact on real-time system performance since a tuned RTVM should have very few vmexits.
You can disable vmexit data collection using the ACRN shell’s vmexit disable
command.
The vmexit command with no arguments (or with a <vm_id> argument) shows a
table of counters for each vmexit reason, for all VM’s (or just the
specified VM’s) vCPUs, showing the latency time counts. For example:
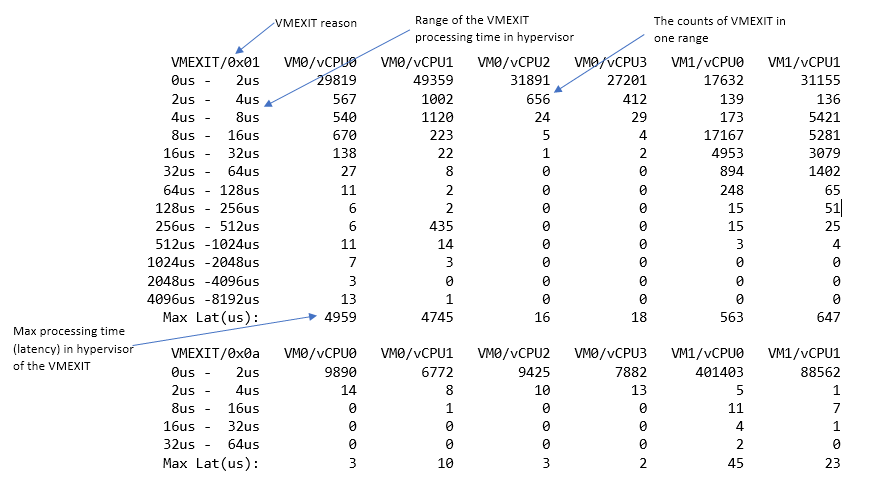
VMexit reason codes are defined in the (ACRN) kernel source code hypervisor/include/arch/x86/asm/vmx.h (search for “VM exit reasons”). Here are a few examples:
VMexit reason code |
Explanation |
|---|---|
0x01 |
An external interrupt (IRQ) arrived |
0x0a |
The guest VM software attempted to execute the CPUID instruction. |
0x0c |
The guest VM attempted to execute HLT instruction. |
0x12 |
The execution of VMCALL by the guest VM caused an ordinary VM exit. |