Virtual Cache Allocation Technology (vCAT)¶
vCAT refers to the virtualization of Cache Allocation Technology (CAT), one of the RDT (Resource Director Technology) technologies.
ACRN vCAT is built on top of ACRN RDT: ACRN RDT provides a number of physical CAT resources (COS IDs + cache ways), ACRN vCAT exposes some number of virtual CAT resources to VMs and then transparently map them to the assigned physical CAT resources in the ACRN hypervisor; VM can take advantage of vCAT to prioritize and partition virtual cache ways for its own tasks.
In current CAT implementation, one COS ID corresponds to one IA32_type_MASK_n (type: L2 or L3,
n ranges from 0 to MAX_CACHE_CLOS_NUM_ENTRIES - 1) MSR and a bit in a capacity bitmask (CBM)
corresponds to one cache way.
On current generation systems, normally L3 cache is shared by all CPU cores on the same socket and L2 cache is generally just shared by the hyperthreads on a core. But when dealing with ACRN vCAT COS IDs assignment, it is assumed that all the L2/L3 caches (and therefore all COS IDs) are system-wide caches shared by all cores in the system, this is done for convenience and to simplify the vCAT configuration process. If vCAT is enabled for a VM (abbreviated as vCAT VM), there should not be any COS ID overlap between a vCAT VM and any other VMs. e.g. the vCAT VM has exclusive use of the assigned COS IDs. When assigning cache ways, however, the VM can be given exclusive, shared, or mixed access to the cache ways depending on particular performance needs. For example, use dedicated cache ways for RTVM, and use shared cache ways between low priority VMs.
In ACRN, the CAT resources allocated for vCAT VMs are determined in Enable Intel Resource Director Technology (RDT) Configurations.
For further details on the RDT, refer to the ACRN RDT high-level design RDT Allocation Feature Supported by Hypervisor.
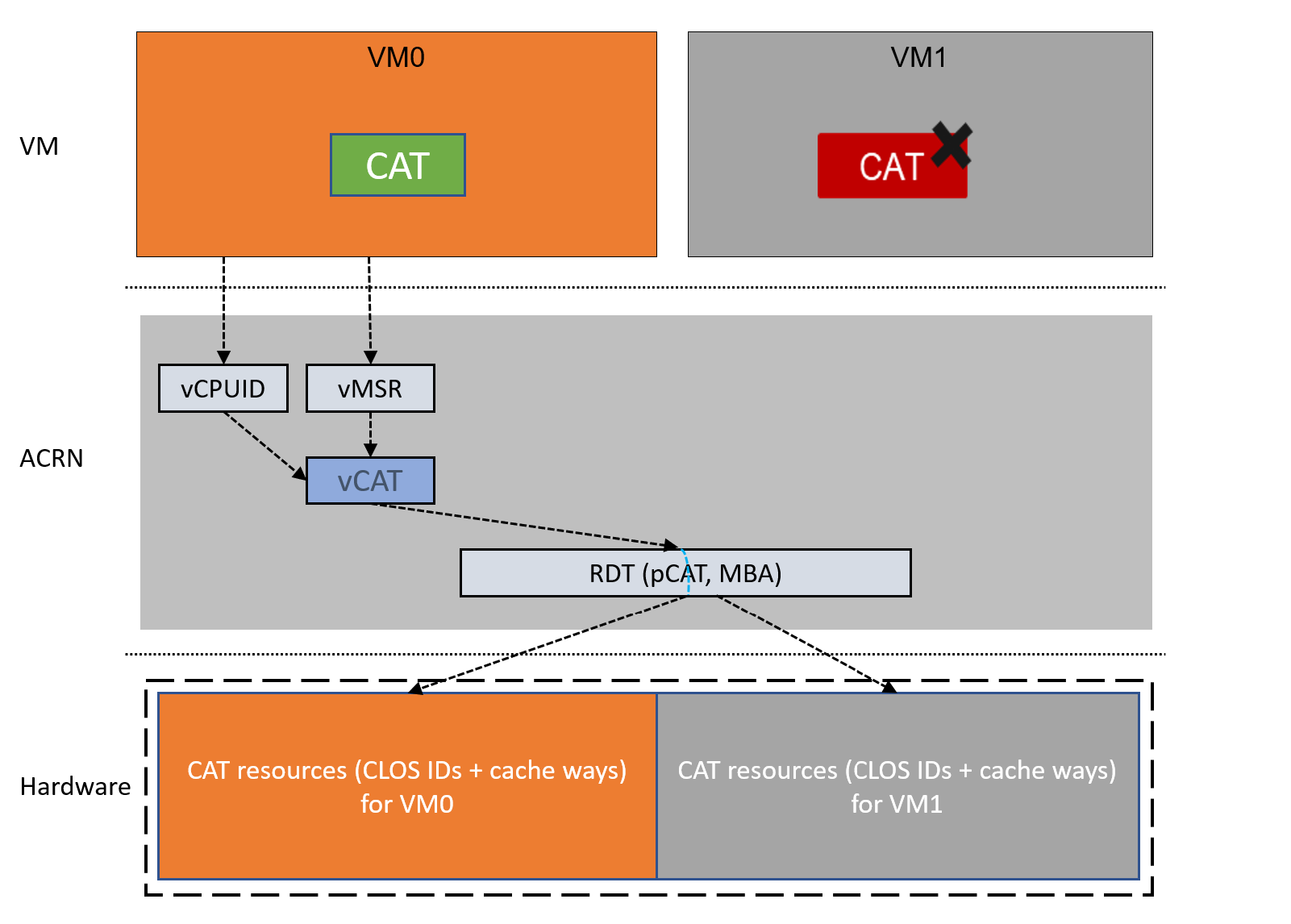
High Level ACRN vCAT Design¶
ACRN CAT virtualization support can be divided into two parts:
CAT Capability Exposure to Guest VM
CAT resources (COS IDs + cache ways) management
The figure below shows high-level design of vCAT in ACRN:
CAT Capability Exposure to Guest VM¶
ACRN exposes CAT capability and resource to a Guest VM via vCPUID and vMSR, as explained in the following sections.
vCPUID¶
CPUID Leaf 07H¶
CPUID.(EAX=07H, ECX=0).EBX.PQE[bit 15]: Supports RDT capability if 1. This bit will be set for a vCAT VM.
CPUID Leaf 10H¶
CAT Resource Type and Capability Enumeration
CPUID.(EAX=10H, ECX=0):EBX[1]: If 1, indicate L3 CAT support for a vCAT VM.
CPUID.(EAX=10H, ECX=0):EBX[2]: If 1, indicate L2 CAT support for a vCAT VM.
CPUID.(EAX=10H, ECX=1): CAT capability enumeration sub-leaf for L3. Reports L3 COS_MAX and CBM_LEN to a vCAT VM
CPUID.(EAX=10H, ECX=2): CAT capability enumeration sub-leaf for L2. Reports L2 COS_MAX and CBM_LEN to a vCAT VM
vMSR¶
The following CAT MSRs will be virtualized for a vCAT VM:
IA32_PQR_ASSOC
IA32_type_MASK_0 ~ IA32_type_MASK_n
By default, after reset, all CPU cores are assigned to COS 0 and all IA32_type_MASK_n MSRs are programmed to allow fill into all cache ways.
CAT resources (COS IDs + cache ways) management¶
All accesses to the CAT MSRs are intercepted by vMSR and control is passed to vCAT, which will perform the following actions:
Intercept IA32_PQR_ASSOC MSR to re-map virtual COS ID to physical COS ID. Upon writes, store the re-mapped physical COS ID into its vCPU
msr_store_areadata structure guest part. It will be loaded to physical IA32_PQR_ASSOC on each VM-Enter.Intercept IA32_type_MASK_n MSRs to re-map virtual CBM to physical CBM. Upon writes, program re-mapped physical CBM into corresponding physical IA32_type_MASK_n MSR
Several vCAT P2V (physical to virtual) and V2P (virtual to physical) mappings exist, as illustrated in the following pseudocode:
struct acrn_vm_config *vm_config = get_vm_config(vm_id)
max_pcbm = vm_config->max_type_pcbm (type: l2 or l3)
mask_shift = ffs64(max_pcbm)
vcosid = vmsr - MSR_IA32_type_MASK_0
pcosid = vm_config->pclosids[vcosid]
pmsr = MSR_IA32_type_MASK_0 + pcosid
pcbm = vcbm << mask_shift
vcbm = pcbm >> mask_shift
- Where
vm_config->pclosids[]: array of physical COS IDs, where each corresponds to onevcpu_closthat is defined in the scenario filemax_pcbm: a bitmask that selects all the physical cache ways assigned to the VM, corresponds to the nthCLOS_MASKthat is defined in scenario file, where n = the first physical COS ID assigned =vm_config->pclosids[0]ffs64(max_pcbm): find the first (least significant) bit set inmax_pcbmand return the index of that bit.MSR_IA32_type_MASK_0: 0xD10 for L2, 0xC90 for L3vcosid: virtual COS ID, always starts from 0pcosid: corresponding physical COS ID for a givenvcosidvmsr: virtual MSR address, passed to vCAT handlers by the caller functionsrdmsr_vmexit_handler()/wrmsr_vmexit_handler()pmsr: physical MSR addressvcbm: virtual CBM, passed to vCAT handlers by the caller functionsrdmsr_vmexit_handler()/wrmsr_vmexit_handler()pcbm: physical CBM