Enable vUART Configurations¶
Introduction¶
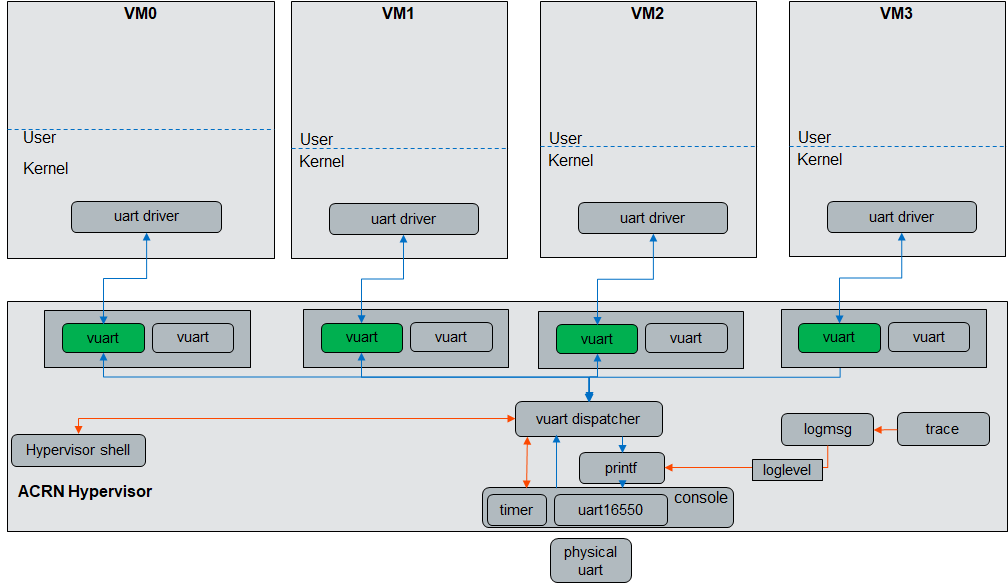
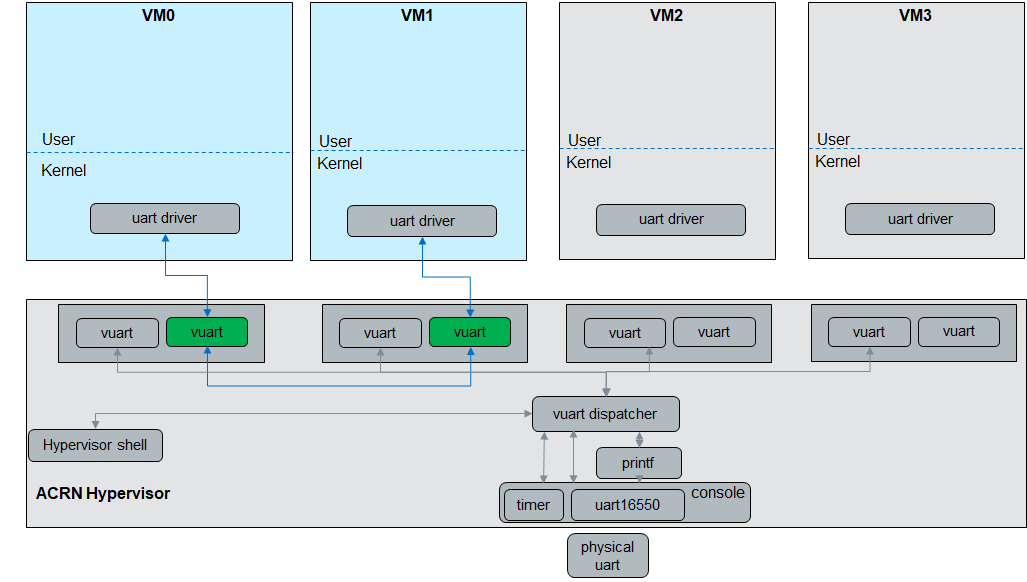
The virtual universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (vUART) supports two functions: one is the console, the other is communication. vUART only works on a single function.
Only two vUART configurations are added to the predefined scenarios, but you can customize the scenarios to enable more using the ACRN configuration toolset.
Console Enable List¶
Scenarios |
vm0 |
vm1 |
vm2 |
vm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SDC |
Service VM (vUART enable) |
Post-launched |
Post-launched |
|
Hybrid |
Pre-launched (Zephyr) (vUART enable) |
Service VM (vUART enable) |
Post-launched |
|
Industry |
Service VM (vUART enable) |
Post-launched |
Post-launched (vUART enable) |
Post-launched |
Logic_partition |
Pre-launched (vUART enable) |
Pre-launched RTVM (vUART enable) |
Post-launched RTVM |
How to Configure a Console Port¶
To enable the console port for a VM, change only the port_base and
irq. If the IRQ number is already in use in your system (cat
/proc/interrupt), choose another IRQ number. If you set the .irq =0,
the vUART will work in polling mode.
COM1_BASE (0x3F8) + COM1_IRQ(4)COM2_BASE (0x2F8) + COM2_IRQ(3)COM3_BASE (0x3E8) + COM3_IRQ(6)COM4_BASE (0x2E8) + COM4_IRQ(7)
Example:
.vuart[0] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM1_BASE,
.irq = COM1_IRQ,
},
How to Configure a Communication Port¶
To enable the communication port, configure vuart[1] in the two VMs that want to communicate.
The port_base and IRQ should differ from the vuart[0] in the same VM.
t_vuart.vm_id is the target VM’s vm_id, start from 0. (0 means VM0)
t_vuart.vuart_id is the target vUART index in the target VM. Start
from 1. (1 means vuart[1])
Example:
/* VM0 */
...
/* VM1 */
.vuart[1] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM2_BASE,
.irq = COM2_IRQ,
.t_vuart.vm_id = 2U,
.t_vuart.vuart_id = 1U,
},
...
/* VM2 */
.vuart[1] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM2_BASE,
.irq = COM2_IRQ,
.t_vuart.vm_id = 1U,
.t_vuart.vuart_id = 1U,
},
Communication vUART Enable List¶
Scenarios |
vm0 |
vm1 |
vm2 |
vm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SDC |
Service VM |
Post-launched |
Post-launched |
|
Hybrid |
Pre-launched (Zephyr) (vUART enable COM2) |
Service VM (vUART enable COM2) |
Post-launched |
|
Industry |
Service VM (vUART enable COM2) |
Post-launched |
Post-launched RTVM (vUART enable COM2) |
Post-launched |
Logic_partition |
Pre-launched |
Pre-launched RTVM |
Launch Script¶
-s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdioThis option is only needed for WaaG and VxWorks (and also when using OVMF). They depend on the ACPI table, and onlyacrn-dmcan provide the ACPI table for UART.-B " ....,console=ttyS0, ..."Add this to the kernel-based system.
Test the Communication Port¶
After you have configured the communication port in hypervisor, you can access the corresponding port. For example, in Linux OS:
With
echoandcatOn VM1:
# cat /dev/ttyS1On VM2:
# echo "test test" > /dev/ttyS1You can find the message from VM1
/dev/ttyS1.If you are not sure which one is the communication port, you can run
dmesg | grep ttySunder the Linux shell to check the base address. If it matches what you have set in thevm_configuration.cfile, it is the correct port.With Minicom
Run
minicom -D /dev/ttyS1on both VM1 and VM2 and entertestin VM1’s Minicom. The message should appear in VM2’s Minicom. Disable flow control in Minicom.Limitations
The msg cannot be longer than 256 bytes.
- This cannot be used to transfer files because flow control is
not supported so data may be lost.
COM Port Configurations for Post-Launched VMs¶
For a post-launched VM, the acrn-dm cmdline also provides a COM port configuration:
-s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio
This adds com1 (0x3f8) and com2 (0x2f8) modules in the Guest VM, including the ACPI info for these two ports.
Data Flows
Three different data flows exist based on how the post-launched VM is started, as shown in the diagram below:
Figure 1 data flow: The post-launched VM is started with the vUART enabled in the hypervisor configuration file only.
Figure 2 data flow: The post-launched VM is started with the
acrn-dmcmdline of-s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdioonly.Figure 3 data flow: The post-launched VM is started with both vUART enabled and the
acrn-dmcmdline of-s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio.
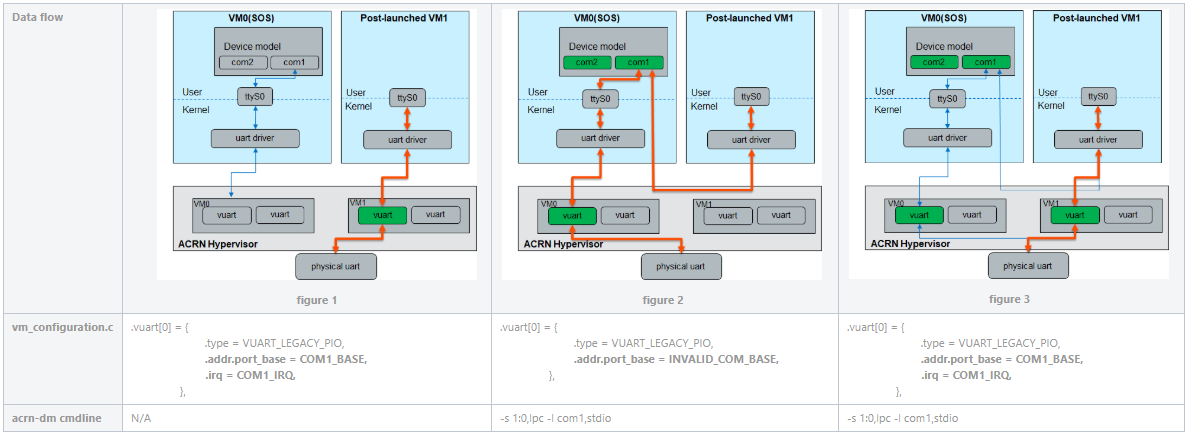
Note
For operating systems such as VxWorks and Windows that depend on the ACPI table to probe the UART driver, adding the vUART configuration in the hypervisor is not sufficient. We recommend that you use the configuration in the figure 3 data flow. This may be refined in the future.
Use PCI-vUART¶
PCI Interface of ACRN vUART¶
When you set vuart[0] and vuart[1], the ACRN
hypervisor emulates virtual legacy serial devices (I/O port and IRQ) for
VMs. So vuart[0] and vuart[1] are legacy vUARTs. ACRN
hypervisor can also emulate virtual PCI serial devices (BDF, MMIO
registers and MSIX capability). These virtual PCI serial devices are
called PCI-vUART, and have an advantage in device enumeration for the
guest OS. It is easy to add new PCI-vUART ports to a VM.
Index of vUART¶
ACRN hypervisor supports PCI-vUARTs and legacy vUARTs as ACRN vUARTs.
Each vUART port has its own vuart_idx. ACRN hypervisor supports up
to 8 vUART for each VM, from vuart_idx=0 to vuart_idx=7.
Suppose we use vUART0 for a port with vuart_idx=0, vUART1 for
vuart_idx=1, and so on.
Pay attention to these points:
vUART0 is the console port, vUART1-vUART7 are inter-VM communication ports.
Each communication port must set the connection to another communication vUART port of another VM.
When legacy
vuart[0]is available, it is vUART0. A PCI-vUART can’t be vUART0 unlessvuart[0]is not set.When legacy
vuart[1]is available, it is vUART1. PCI-vUART can’t be vUART1 unlessvuart[1]is not set.
Setup ACRN vUART Using Configuration Tools¶
When you set up ACRN VM configurations with PCI-vUART, it is better to
use the ACRN configuration tools because of all the PCI resources required: BDF number,
address and size of mmio registers, and address and size of MSIX entry
tables. These settings can’t conflict with another PCI device. Furthermore,
whether PCI-vUART can use vuart_idx=0 and vuart_idx=1 depends on legacy
vUART settings. Configuration tools will override your settings in
How to Configure a Console Port
and How to Configure a Communication Port.
You can configure both Legacy vUART and PCI-vUART in scenario configurations. For example, if VM0 has a legacy vUART0 and a PCI-vUART1, VM1 has no legacy vUART but has a PCI-vUART0 and a PCI-vUART1, VM0’s PCI-vUART1 and VM1’s PCI-vUART1 are connected to each other. You should configure then like this:
<vm id="0">
<legacy_vuart id="0">
<type>VUART_LEGACY_PIO</type> /* vuart[0] is console port */
<base>COM1_BASE</base> /* vuart[0] is used */
<irq>COM1_IRQ</irq>
</legacy_vuart>
<legacy_vuart id="1">
<type>VUART_LEGACY_PIO</type>
<base>INVALID_COM_BASE</base> /* vuart[1] is not used */
</legacy_vuart>
<console_vuart id="0">
<base>INVALID_PCI_BASE</base> /* PCI-vUART0 can't be used, because vuart[0] */
</console_vuart>
<communication_vuart id="1">
<base>PCI_VUART</base> /* PCI-vUART1 is communication port, connect to vUART1 of VM1 */
<target_vm_id>1</target_vm_id>
<target_uart_id>1</target_uart_id>
</communication_vuart>
</vm>
<vm id="1">
<legacy_vuart id="0">
<type>VUART_LEGACY_PIO</type>
<base>INVALID_COM_BASE</base> /* vuart[0] is not used */
</legacy_vuart>
<legacy_vuart id="1">
<type>VUART_LEGACY_PIO</type>
<base>INVALID_COM_BASE</base> /* vuart[1] is not used */
</legacy_vuart>
<console_vuart id="0">
<base>PCI_VUART</base> /* PCI-vUART0 is console port */
</console_vuart>
<communication_vuart id="1">
<base>PCI_VUART</base> /* PCI-vUART1 is communication port, connect to vUART1 of VM0 */
<target_vm_id>0</target_vm_id>
<target_uart_id>1</target_uart_id>
</communication_vuart>
</vm>
The ACRN vUART related XML fields:
idin<legacy_vuart>, value ofvuart_idx,id=0is for legacyvuart[0]configuration,id=1is forvuart[1].
typein<legacy_vuart>, type is alwaysVUART_LEGACY_PIOfor legacy vUART.
basein<legacy_vuart>, if using the legacy vUART port, set COM1_BASE forvuart[0], setCOM2_BASEforvuart[1].INVALID_COM_BASEmeans do not use the legacy vUART port.
irqin<legacy_vuart>, if you use the legacy vUART port, setCOM1_IRQforvuart[0], setCOM2_IRQforvuart[1].
idin<console_vuart>and<communication_vuart>,vuart_idxfor PCI-vUART
basein<console_vuart>and<communication_vuart>,PCI_VUARTmeans use this PCI-vUART,INVALID_PCI_BASEmeans do not use this PCI-VUART.
target_vm_idandtarget_uart_id, connection settings for this vUART port.
Run the command to build ACRN with this XML configuration file:
make BOARD=<board> SCENARIO=<scenario>
The configuration tools will test your settings, and check vUART
Rules for compilation issue. After compiling, you can find
the generated sources under
build/hypervisor/configs/scenarios/<scenario>/pci_dev.c,
based on the XML settings, something like:
struct acrn_vm_pci_dev_config vm0_pci_devs[] = {
{
.emu_type = PCI_DEV_TYPE_HVEMUL,
.vbdf.bits = {.b = 0x00U, .d = 0x05U, .f = 0x00U},
.vdev_ops = &vmcs9900_ops,
.vbar_base[0] = 0x80003000,
.vbar_base[1] = 0x80004000,
.vuart_idx = 1, /* PCI-vUART1 of VM0 */
.t_vuart.vm_id = 1U, /* connected to VM1's vUART1 */
.t_vuart.vuart_id = 1U,
},
}
This struct shows a PCI-vUART with vuart_idx=1, BDF 00:05.0, it’s
a PCI-vUART1 of
VM0, and it is connected to VM1’s vUART1 port. When VM0 wants to communicate
with VM1, it can use /dev/ttyS*, the character device file of
VM0’s PCI-vUART1. Usually, legacy vuart[0] is ttyS0 in VM, and
vuart[1] is ttyS1. So we hope PCI-vUART0 is ttyS0,
PCI-VUART1 is ttyS1 and so on through
PCI-vUART7 is ttyS7, but that is not true. We can use BDF to identify
PCI-vUART in VM.
If you run dmesg | grep tty at a VM shell, you may see:
[ 1.276891] 0000:00:05.0: ttyS4 at MMIO 0xa1414000 (irq = 124, base_baud = 115200) is a 16550A
We know for VM0 guest OS, ttyS4 has BDF 00:05.0 and is PCI-vUART1.
VM0 can communicate with VM1 by reading from or writing to /dev/ttyS4.
If VM0 and VM1 are pre-launched VMs, or Service VM, ACRN hypervisor will
create PCI-vUART virtual devices automatically. For post-launched VMs,
created by acrn-dm, an additional acrn-dm option is needed
to create a PCI-vUART virtual device:
-s <slot>,uart,vuart_idx:<val>
Kernel Config for Legacy vUART¶
When ACRN hypervisor passthroughs a local APIC to a VM, there is IRQ injection issue for legacy vUART. The kernel driver must work in polling mode to avoid the problem. The VM kernel should have these config symbols set:
CONFIG_SERIAL_8250_EXTENDED=y
CONFIG_SERIAL_8250_DETECT_IRQ=y
Kernel Cmdline for PCI-vUART Console¶
When an ACRN VM does not have a legacy vuart[0] but has a
PCI-vUART0, you can use PCI-vUART0 for VM serial input/output. Check
which TTY has the BDF of PCI-vUART0; usually it is not /dev/ttyS0.
For example, if /dev/ttyS4 is PCI-vUART0, you must set
console=/dev/ttyS4 in the kernel cmdline.