Trusty TEE¶
Introduction¶
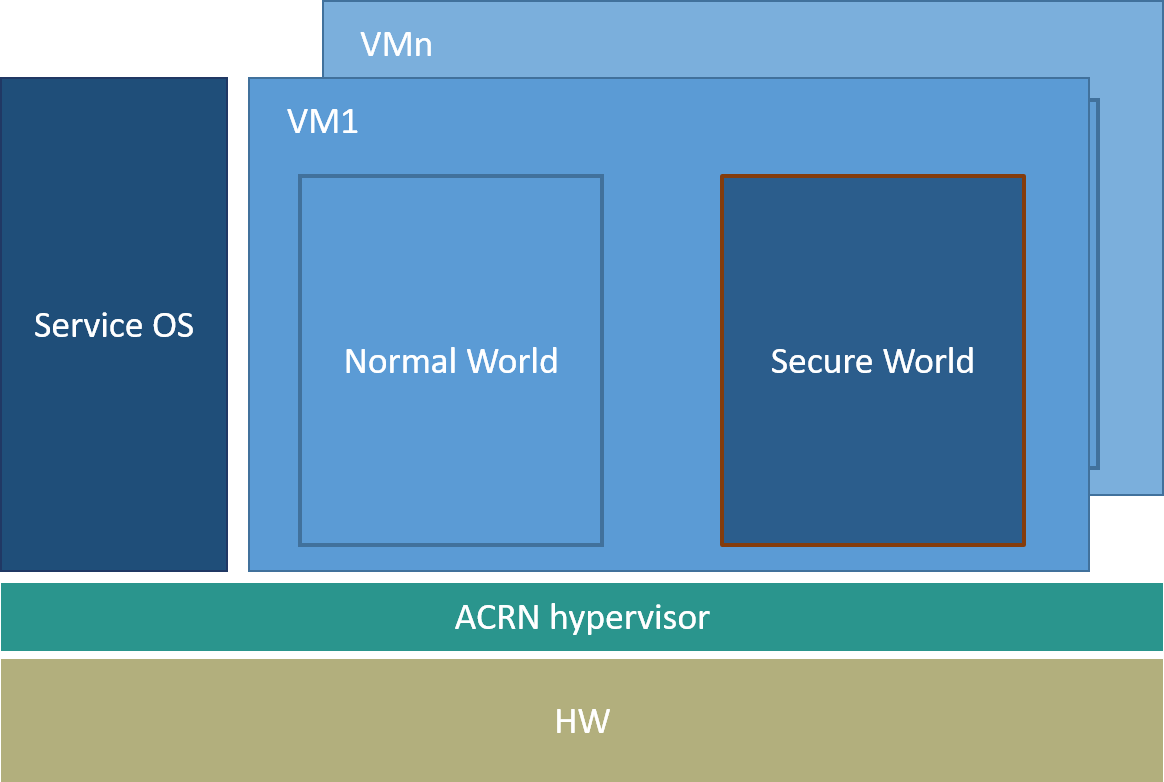
Trusty is a set of software components supporting a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). TEE is commonly known as an isolated processing environment in which applications can be securely executed irrespective of the rest of the system. For more information about TEE, visit the Trusted Execution Environment wiki page. Trusty consists of:
An operating system (the Trusty OS) that runs on a processor intended to provide a TEE
Drivers for the Android kernel (Linux) to facilitate communication with applications running under the Trusty OS
A set of libraries for Android/Linux systems software to facilitate communication with trusted applications executed within the Trusty OS using the kernel drivers
LK (Little Kernel) is a tiny operating system suited for small embedded devices, bootloaders, and other environments where OS primitives such as threads, mutexes, and timers are needed, but there’s a desire to keep things small and lightweight. LK has been chosen as the Trusty OS kernel.
Trusty Specific Hypercalls¶
There are a few Hypercall APIs that are related to Trusty.
-
int32_t
hcall_world_switch(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, struct acrn_vm *target_vm, uint64_t param1, uint64_t param2)¶ Switch vCPU state between Normal/Secure World.
The hypervisor uses this hypercall to do the world switch
The hypervisor needs to:
save current world vCPU contexts, and load the next world vCPU contexts
update
rdi,rsi,rdx,rbxto next world vCPU contexts
- Return
0 on success, non-zero on error.
- Parameters
vcpu: Pointer to VCPU data structuretarget_vm: not usedparam1: not usedparam2: not used
-
int32_t
hcall_initialize_trusty(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, struct acrn_vm *target_vm, uint64_t param1, uint64_t param2)¶ Initialize environment for Trusty-OS on a vCPU.
It is used by the User OS bootloader (
UOS_Loader) to request ACRN to initialize TrustyThe Trusty memory region range, entry point must be specified
The hypervisor needs to save current vCPU contexts (Normal World)
- Return
0 on success, non-zero on error.
- Parameters
vcpu: Pointer to vCPU data structuretarget_vm: not usedparam1: guest physical address. This gpa points to trusty_boot_param structureparam2: not used
-
int32_t
hcall_save_restore_sworld_ctx(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, struct acrn_vm *target_vm, uint64_t param1, uint64_t param2)¶ Save/Restore Context of Secure World.
- Return
0 on success, non-zero on error.
- Parameters
vcpu: Pointer to VCPU data structuretarget_vm: not usedparam1: not usedparam2: not used
Trusty Boot Flow¶
By design, the User OS bootloader (UOS_Loader) will trigger the Trusty
boot process. The complete boot flow is illustrated below.
![digraph G {
rankdir=LR;
rank=same;
bgcolor="transparent";
uosl1 [label="UOS_Loader"]
acrn_init [shape=box style="rounded,filled" label="ACRN"]
acrn_switch [shape=box style="rounded,filled" label="ACRN"]
uosl2 [label="UOS_Loader"]
uosl1 -> acrn_init -> "Trusty" -> acrn_switch -> uosl2;
}](../_images/graphviz-e6e2a1eec282a0115edca464cd66d9cc483da268.png)
Figure 279 Trusty Boot Flow¶
As shown in the above figure, here are some details about the Trusty boot flow processing:
UOS_Loader
Load and verify Trusty image from virtual disk
Allocate runtime memory for trusty
Do ELF relocation of trusty image and get entry address
Call
hcall_initialize_trustywith trusty memory base and entry address
ACRN (
hcall_initialize_trusty)Save World context for Normal World
Init World context for Secure World (RIP, RSP, EPT, etc.)
Resume to Secure World
Trusty
Booting
Call
hcall_world_switchto switch back to Normal World if boot completed
ACRN (
hcall_world_switch)Save World context for the World that caused this
vmexit(Secure World)Restore World context for next World (Normal World (UOS_Loader))
Resume to next World (UOS_Loader)
UOS_Loader
Continue to boot
EPT Hierarchy¶
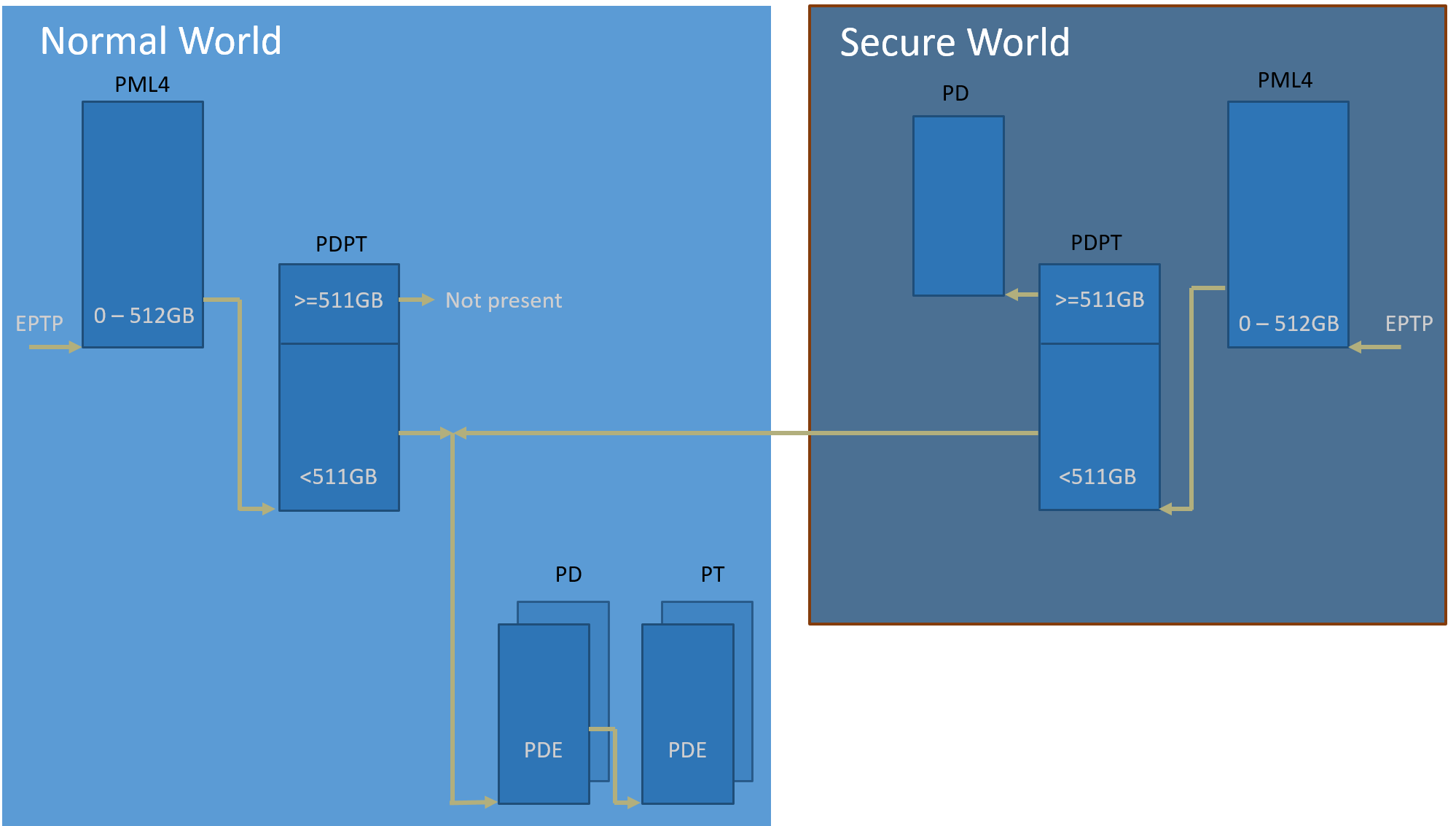
As per the Trusty design, Trusty can access Normal World’s memory, but Normal World cannot access Secure World’s memory. Hence it means Secure World EPTP page table hierarchy must contain normal world GPA address space, while Trusty world’s GPA address space must be removed from the Normal world EPTP page table hierarchy.
Design¶
Put Secure World’s GPA to very high position: 511 GB - 512 GB. The PML4/PDPT for Trusty World are separated from Normal World. PD/PT for low memory (< 511 GB) are shared in both Trusty World’s EPT and Normal World’s EPT. PD/PT for high memory (>= 511 GB) are valid for Trusty World’s EPT only.
Benefit¶
This design will benefit the EPT changes of Normal World. There are requirements to modify Normal World’s EPT during runtime such as increasing memory, changing attributes, etc. If such behavior happened, only PD and PT for Normal World need to be updated.
API¶
-
void
create_secure_world_ept(struct acrn_vm *vm, uint64_t gpa_orig, uint64_t size, uint64_t gpa_rebased)¶ Create Secure World EPT hierarchy.
Create Secure World EPT hierarchy, construct new PML4/PDPT, reuse PD/PT parse from vm->arch_vm->ept
- Parameters
vm: pointer to a VM with 2 Worldsgpa_orig: original gpa allocated from vSBLsize: LK size (16M by default)gpa_rebased: gpa rebased to offset xxx (511G_OFFSET)
-
void
destroy_secure_world(struct acrn_vm *vm, bool need_clr_mem)¶
-
void
save_world_ctx(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, struct ext_context *ext_ctx)¶
-
void
load_world_ctx(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, const struct ext_context *ext_ctx)¶
-
void
copy_smc_param(const struct run_context *prev_ctx, struct run_context *next_ctx)¶
-
void
switch_world(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, int32_t next_world)¶
-
bool
setup_trusty_info(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, uint32_t mem_size, uint64_t mem_base_hpa, uint8_t *rkey)¶
-
bool
init_secure_world_env(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, uint64_t entry_gpa, uint64_t base_hpa, uint32_t size, uint8_t *rpmb_key)¶
-
bool
initialize_trusty(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu, struct trusty_boot_param *boot_param)¶
-
void
save_sworld_context(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu)¶
-
void
restore_sworld_context(struct acrn_vcpu *vcpu)¶