Enable S5 in ACRN¶
Introduction¶
S5 is one of the ACPI sleep states that refers to the system being shut down (although some power may still be supplied to certain devices). In this document, S5 means the function to shut down the User VMs, the Service VM, the hypervisor, and the hardware. In most cases, directly shutting down the power of a computer system is not advisable because it can damage some components. It can cause corruption and put the system in an unknown or unstable state. On ACRN, the User VM must be shut down before powering off the Service VM. Especially for some use cases, where User VMs could be used in industrial control or other high safety requirement environment, a graceful system shutdown such as the ACRN S5 function is required.
S5 Architecture¶
ACRN provides a mechanism to trigger the S5 state transition throughout the system. It uses a vUART channel to communicate between the Service and User VMs. The diagram below shows the overall architecture:
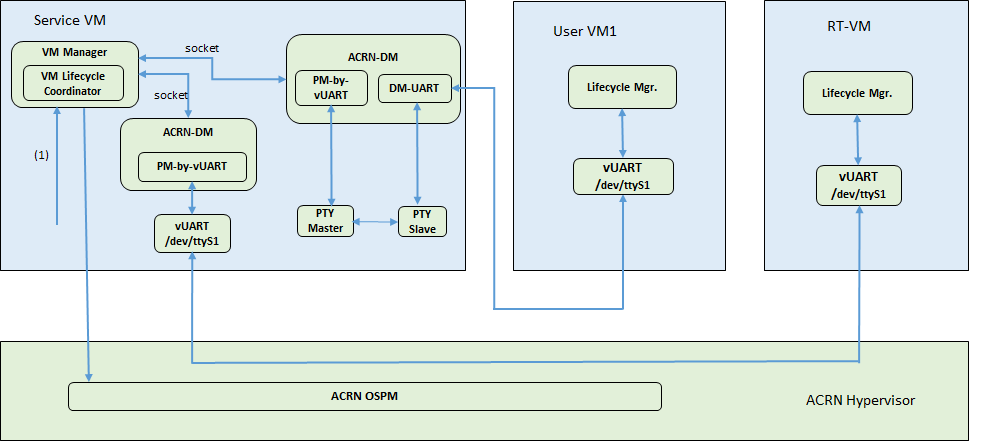
Figure 28 S5 overall architecture¶
Scenario I:
The User VM’s serial port device (
ttySn) is emulated in the Device Model, the channel from the Service VM to the User VM:![digraph G {
node [shape=plaintext fontsize=12];
graph [rankdir=LR];
subgraph cluster_0 {
node [shape=box];
label="PTY"
"Master" -> "Slave" [dir=both arrowsize=.5];
}
"ACRN-DM" -> "Master" [arrowsize=.5];
"Slave" -> "User VM:/dev/ttyS1" [arrowsize=.5];
}](../_images/graphviz-976454e2b56c6477c237bf5ced77562e08ab0361.png)
Scenario II:
The User VM’s (like RT-Linux or other RT-VMs) serial port device (
ttySn) is emulated in the Hypervisor, the channel from the Service OS to the User VM:![digraph G {
node [shape=plaintext fontsize=12];
rankdir=LR;
bgcolor="transparent";
"ACRN-DM" -> "Service VM:/dev/ttyS1" -> "ACRN hypervisor" -> "User VM:/dev/ttyS1" [arrowsize=.5];
}](../_images/graphviz-e1efa2c636ae3a0d3d6ebb7391fa26265ac502c7.png)
Initiate a system S5 from within a User VM (e.g. HMI)¶
As in Figure 56, a request to Service VM initiates the shutdown flow. This could come from a User VM, most likely the HMI (Windows or user-friendly Linux). When a human operator click to initiate the flow, the lifecycle_mgr in it will send the request via vUART to the lifecycle manager in the Service VM which in turn acknowledge the request and trigger the following flow.
Note
The User VM need to be authorized to be able to request a Shutdown, this is achieved by adding
“--pm_notify_channel uart,allow_trigger_s5” in the launch script of that VM.
And, there is only one VM in the system can be configured to request a shutdown. If there is a second User
VM launched with “--pm_notify_channel uart,allow_trigger_s5”, ACRN will stop launching it and throw
out below error message:
initiate a connection on a socket error
create socket to connect life-cycle manager failed
Trigger the User VM’s S5¶
On the Service VM side, it uses the acrnctl tool to trigger the User VM’s S5 flow:
acrnctl stop user-vm-name. Then, the Device Model sends a shutdown command
to the User VM through a channel. If the User VM receives the command, it will send an “ACK”
to the Device Model. It is the Service VM’s responsibility to check if the User VMs
shut down successfully or not, and decides when to power off itself.
User VM “Lifecycle Manager”¶
As part of the current S5 reference design, a lifecycle manager daemon (life_mngr) runs in the
User VM to implement S5. It waits for the command from the Service VM on the
paired serial port. The simple protocol between the Service VM and User VM is as follows:
When the daemon receives shutdown, it sends “ACKed” to the Service VM;
then it can power off the User VM. If the User VM is not ready to power off,
it can ignore the shutdown command.
Enable S5¶
The procedure for enabling S5 is specific to the particular OS:
For Linux (LaaG) or Windows (WaaG), refer to the following configurations in the
misc/config_tools/data/sample_launch_scripts/nuc/launch_uos.shlaunch script foracrn-dm.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
-s 3,virtio-blk,/home/clear/uos/uos.img \ -s 4,virtio-net,tap0 \ -s 7,virtio-rnd \ --ovmf /usr/share/acrn/bios/OVMF.fd \ $logger_setting \ --mac_seed $mac_seed \ $vm_name } #add following cmdline to grub.cfg and update kernel #when launching LaaG by OVMF #rw rootwait maxcpus=1 nohpet console=tty0 console=hvc0 #console=ttyS0 no_timer_check ignore_loglevel #log_buf_len=16M consoleblank=0 #tsc=reliable i915.avail_planes_per_pipe="64 448 8" #i915.enable_hangcheck=0 i915.nuclear_pageflip=1 #i915.enable_guc_loading=0 #i915.enable_guc_submission=0 i915.enable_guc=0 # offline SOS CPUs except BSP before launch UOS for i in `ls -d /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu[1-99]`; do
For RT-Linux, refer to the
misc/config_tools/data/sample_launch_scripts/nuc/launch_hard_rt_vm.shscript:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
/usr/bin/acrn-dm -A -m $mem_size -s 0:0,hostbridge \ --lapic_pt \ --rtvm \ --virtio_poll 1000000 \ -U 495ae2e5-2603-4d64-af76-d4bc5a8ec0e5 \ -s 2,passthru,02/0/0 \ -s 3,virtio-console,@stdio:stdio_port \ --ovmf /usr/share/acrn/bios/OVMF.fd \ hard_rtvm } # -s 2,passthru,0/17/0 \ #please using "lspci -nn" check the bdf info # Depends on which partation RT_LaaG is installed in;maybe need to change # /dev/nvme0n1p3 to /dev/sda3 on NUC and uncomment SATA pass-through
Note
For RT-Linux, the vUART is emulated in the hypervisor; expose the node as
/dev/ttySn.
For LaaG and RT-Linux VMs, run the lifecycle manager daemon:
Use these commands to build the lifecycle manager daemon,
life_mngr.$ cd acrn-hypervisor/misc/life_mngr $ make life_mngr
Copy
life_mngrandlife_mngr.serviceinto the User VM:$ scp life_mngr root@<test board address>:/usr/bin/life_mngr $ scp life_mngr.service root@<test board address>:/lib/systemd/system/life_mngr.service
Use the below commands to enable
life_mngr.serviceand restart the User VM.# chmod +x /usr/bin/life_mngr # systemctl enable life_mngr.service # reboot
For the WaaG VM, run the lifecycle manager daemon:
Build the
life_mngr_win.exeapplication:$ cd acrn-hypervisor/misc $ make life_mngr
Note
If there is no
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcccompiler, you can runsudo apt install gcc-mingw-w64-x86-64on Ubuntu to install it.Set up a Windows environment:
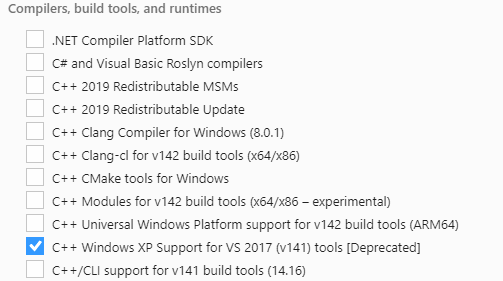
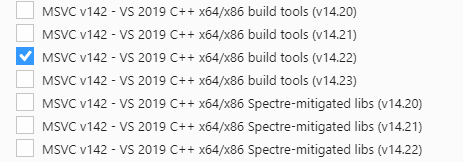
Download the Visual Studio 2019 tool from https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/, and choose the two options in the below screenshots to install “Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2015, 2017 and 2019 (x86 or X64)” in WaaG:
In WaaG, use the Windows + R shortcut key, input
shell:startup, click OK and then copy thelife_mngr_win.exeapplication into this directory.
Restart the WaaG VM. The COM2 window will automatically open after reboot.
If the Service VM is being shut down (transitioning to the S5 state), it can call
acrnctl stop vm-nameto shut down the User VMs.Note
S5 state is not automatically triggered by a Service VM shutdown; this needs to be run before powering off the Service VM.
How to Test¶
As described in Enable vUART Configurations, two vUARTs are defined in pre-defined ACRN scenarios: vUART0/ttyS0 for the console and vUART1/ttyS1 for S5-related communication (as shown in S5 overall architecture).
For Yocto Project (Poky) or Ubuntu rootfs, the
serial-gettyservice forttyS1conflicts with the S5-related communication use ofvUART1. We can eliminate the conflict by preventing that service from being started either automatically or manually, by masking the service using this commandsystemctl mask serial-getty@ttyS1.service
Refer to the Enable S5 section to set up the S5 environment for the User VMs.
Note
RT-Linux’s UUID must use
495ae2e5-2603-4d64-af76-d4bc5a8ec0e5. Also, the industry EFI image is required for launching the RT-Linux VM.Note
Use the
systemctl status life_mngr.servicecommand to ensure the service is working on the LaaG or RT-Linux:* life_mngr.service - ACRN lifemngr daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/life_mngr.service; enabled; vendor p> Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-09-10 07:15:06 UTC; 1min 11s ago Main PID: 840 (life_mngr)
Note
For WaaG, we need to close
windbgby using thebcdedit /set debug offcommand IF you executed thebcdedit /set debug onwhen you set up the WaaG, because it occupies theCOM2.Use the
acrnctl stopcommand on the Service VM to trigger S5 to the User VMs:# acrnctl stop vm1Use the
acrnctl listcommand to check the User VM status.# acrnctl list vm1 stopped
System Shutdown¶
Using a coordinating script, misc/life_mngr/s5_trigger.sh, in conjunction with
the lifecycle manager in each VM, graceful system shutdown can be performed.
Note
Please install s5_trigger.sh manually to root’s home directory.
$ sudo install -p -m 0755 -t ~root misc/life_mngr/s5_trigger.sh
In the hybrid_rt scenario, the script can send a shutdown command via ttyS1
in the Service VM, which is connected to ttyS1 in the pre-launched VM. The
lifecycle manager in the pre-launched VM receives the shutdown command, sends an
ack message, and proceeds to shut itself down accordingly.
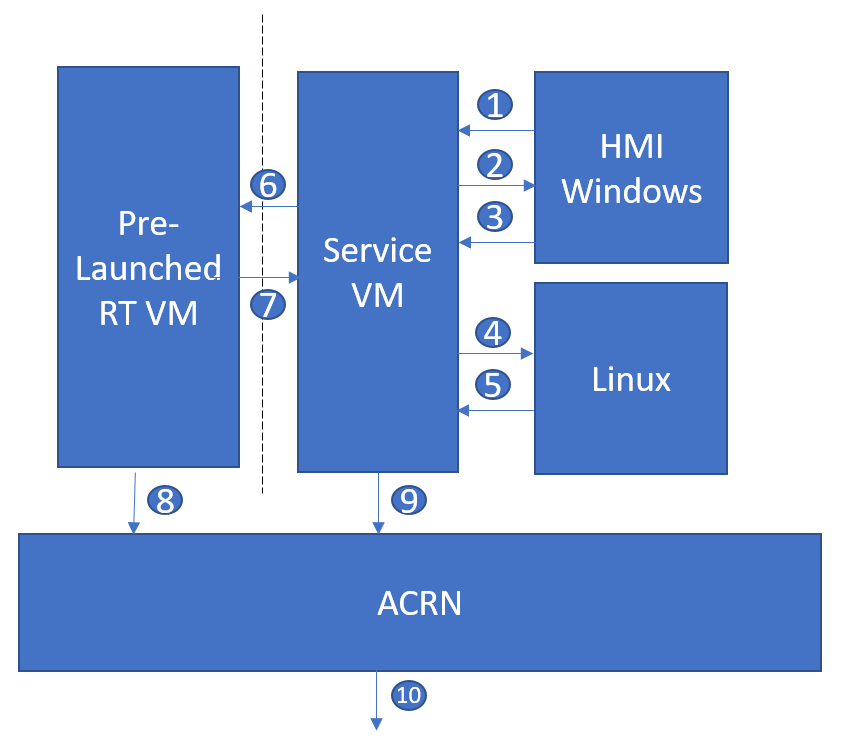
Figure 29 Graceful system shutdown flow¶
The HMI Windows Guest uses the lifecycle manager to send a shutdown request to the Service VM
The lifecycle manager in the Service VM responds with an ack message and executes
s5_trigger.shAfter receiving the ack message, the lifecycle manager in the HMI Windows Guest shuts down the guest
The
s5_trigger.shscript in the Service VM shuts down the Linux Guest by usingacrnctlto send a shutdown requestAfter receiving the shutdown request, the lifecycle manager in the Linux Guest responds with an ack message and shuts down the guest
The
s5_trigger.shscript in the Service VM shuts down the Pre-launched RTVM by sending a shutdown request to itsttyS1After receiving the shutdown request, the lifecycle manager in the Pre-launched RTVM responds with an ack message
The lifecycle manager in the Pre-launched RTVM shuts down the guest using standard PM registers
After receiving the ack message, the
s5_trigger.shscript in the Service VM shuts down the Service VMThe hypervisor shuts down the system after all of its guests have shut down