Virtio-console¶
The Virtio-console is a simple device for data input and output. The
console’s virtio device ID is 3 and can have from 1 to 16 ports.
Each port has a pair of input and output virtqueues used to communicate
information between the Front End (FE) and Back end (BE) drivers.
Currently the size of each virtqueue is 64 (configurable in the source
code). The FE driver will place empty buffers for incoming data onto
the receiving virtqueue, and enqueue outgoing characters onto the
transmitting virtqueue.
A Virtio-console device has a pair of control IO virtqueues as well. The control virtqueues are used to communicate information between the device and the driver, including: ports being opened and closed on either side of the connection, indication from the host about whether a particular port is a console port, adding new ports, port hot-plug/unplug, indication from the guest about whether a port or a device was successfully added, or a port opened or closed.
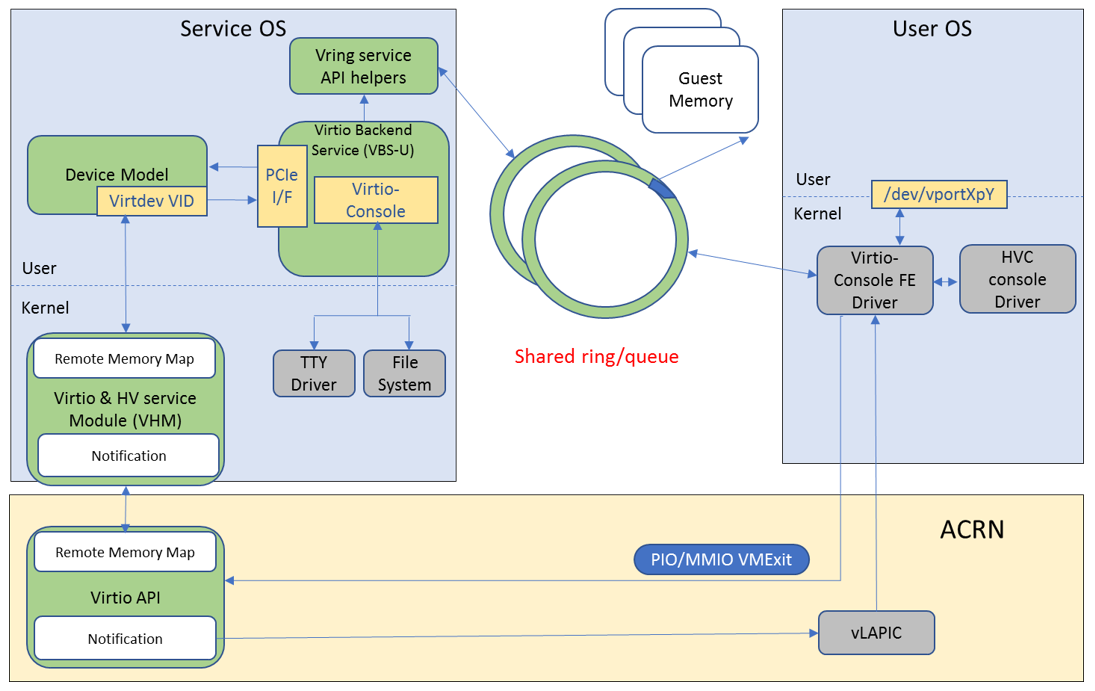
The virtio-console architecture diagram in ACRN is shown below.
Virtio-console is implemented as a virtio legacy device in the ACRN
device model (DM), and is registered as a PCI virtio device to the guest
OS. No changes are required in the frontend Linux virtio-console except
that the guest (User VM) kernel should be built with
CONFIG_VIRTIO_CONSOLE=y.
The virtio console FE driver registers a HVC console to the kernel if
the port is configured as console. Otherwise it registers a char device
named /dev/vportXpY to the kernel, and can be read and written from
the user space. There are two virtqueues for a port, one is for
transmitting and the other is for receiving. The FE driver places empty
buffers onto the receiving virtqueue for incoming data, and enqueues
outgoing characters onto the transmitting virtqueue.
The virtio console BE driver copies data from the FE’s transmitting virtqueue when it receives a kick on the virtqueue (implemented as a vmexit). The BE driver then writes the data to the backend, and can be implemented as PTY, TTY, STDIO, and a regular file. BE driver uses mevent to poll the available data from the backend file descriptor. When new data is available, the BE driver reads it to the receiving virtqueue of the FE, followed by an interrupt injection.
The feature bits currently supported by the BE device are:
| VTCON_F_SIZE(bit 0) | configuration columns and rows are valid. |
| VTCON_F_MULTIPORT(bit 1) | device supports multiple ports, and control virtqueues will be used. |
| VTCON_F_EMERG_WRITE(bit 2) | device supports emergency write. |
Virtio-console supports redirecting guest output to various backend devices. Currently the following backend devices are supported in ACRN device model: STDIO, TTY, PTY and regular file.
The device model configuration command syntax for virtio-console is:
virtio-console,[@]stdio|tty|pty|file:portname[=portpath]\
[,[@]stdio|tty|pty|file:portname[=portpath][:socket_type]]
Preceding with
@marks the port as a console port, otherwise it is a normal virtio serial portThe
portpathcan be omitted when backend is stdio or ptyThe
stdio/tty/ptyis tty capable, which means TAB and BACKSPACE are supported, as on a regular terminalWhen tty is used, please make sure the redirected tty is sleeping, (e.g., by
sleep 2dcommand), and will not read input from stdin before it is used by virtio-console to redirect guest output.When virtio-console socket_type is appointed to client, please make sure server VM(socket_type is appointed to server) has started.
Claiming multiple virtio serial ports as consoles is supported, however the guest Linux OS will only use one of them, through the
console=hvcNkernel parameter. For example, the following command defines two backend ports, which are both console ports, but the frontend driver will only use the second port namedpty_portas its hvc console (specified byconsole=hvc1in the kernel command line):-s n,virtio-console,@tty:tty_port=/dev/pts/0,@pty:pty_port \ -B "root=/dev/vda2 rw rootwait maxcpus=$2 nohpet console=hvc1 console=ttyS0 ..."
Console Backend Use Cases¶
The following sections elaborate on each backend.
STDIO¶
Add a pci slot to the device model (
acrn-dm) command line:-s n,virtio-console,@stdio:stdio_port
Add the
consoleparameter to the guest OS kernel command line:console=hvc0
PTY¶
Add a pci slot to the device model (
acrn-dm) command line:-s n,virtio-console,@pty:pty_port
Add the
consoleparameter to the guest os kernel command line:console=hvc0
One line of information, such as shown below, will be printed in the terminal after
acrn-dmis launched (/dev/pts/0may be different, depending on your use case):virt-console backend redirected to /dev/pts/0Use a terminal emulator, such as minicom or screen, to connect to the tty node:
# minicom -D /dev/pts/0or :
# screen /dev/pts/0
TTY¶
Identify your tty that will be used as the User VM console:
If you’re connected to your device over the network via ssh, use the linux
ttycommand, and it will report the node (may be different in your use case):/dev/pts/0 # sleep 2d
If you do not have network access to your device, use screen to create a new tty:
# screen # tty
you will see (depending on your use case):
/dev/pts/0Prevent the tty from responding by sleeping:
# sleep 2dand detach the tty by pressing CTRL-A d.
Add a pci slot to the device model (
acrn-dm) command line (changing thedev/pts/Xto match your use case):-s n,virtio-console,@tty:tty_port=/dev/pts/X
Add the console parameter to the guest OS kernel command line:
console=hvc0
Go back to the previous tty. For example, if you’re using
screen, use:# screen -ls # screen -r <pid_of_your_tty>
FILE¶
The File backend only supports console output to a file (no input).
Add a pci slot to the device model (
acrn-dm) command line, adjusting the</path/to/file>to your use case:-s n,virtio-console,@file:file_port=</path/to/file>
Add the console parameter to the guest OS kernel command line:
console=hvc0
SOCKET¶
The virtio-console socket-type can be set as socket server or client. Device model will create an unix domain socket if appointed the socket_type as server, then server VM or another user VM can bind and listen for communication requirement. If appointed to client, please make sure the socket server is ready prior to launch device model.
Add a pci slot to the device model (
acrn-dm) command line, adjusting the</path/to/file.sock>to your use case in the VM1 configuration:-s n,virtio-console,socket:socket_file_name=</path/to/file.sock>:server
Add a pci slot to the device model (
acrn-dm) command line, adjusting the</path/to/file.sock>to your use case in the VM2 configuration:-s n,virtio-console,socket:socket_file_name=</path/to/file.sock>:client
Login to VM1, connect to the virtual port(vport1p0, 1 is decided by front-end driver):
# minicom -D /dev/vport1p0Login to VM2, connect to the virtual port(vport3p0, 3 is decided by front-end driver):
# minicom -D /dev/vport3p0Input into minicom window of VM1 or VM2, the minicom window of VM1 will indicate the input from VM2, the minicom window of VM2 will indicate the input from VM1.