Enable QoS based on runC Containers¶
This document describes how ACRN supports Device-Model Quality of Service (QoS) based on using runC containers to control the Service VM resources (CPU, Storage, Memory, Network) by modifying the runC configuration file.
What is QoS¶
Traditionally, Quality of Service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a computer network or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance is seen by the users on the network.
What is runC container¶
Containers are an abstraction at the application layer that packages code and dependencies together. Multiple containers can run on the same machine and share the OS kernel with other containers, each running as isolated processes in user space. runC, a lightweight universal container runtime, is a command-line tool for spawning and running containers according to the Open Container Initiative (OCI) specification.
ACRN-DM QoS architecture¶
In ACRN-DM QoS design, we run the ACRN-DM in a runC container environment. Every time we start a User VM, we first start a runC container and then launch the ACRN-DM within that container. The ACRN-DM QoS can manage these resources for Device-Model:
- CPU utilization
- Memory amount/limitation
- I/O bandwidth
- Network throughput
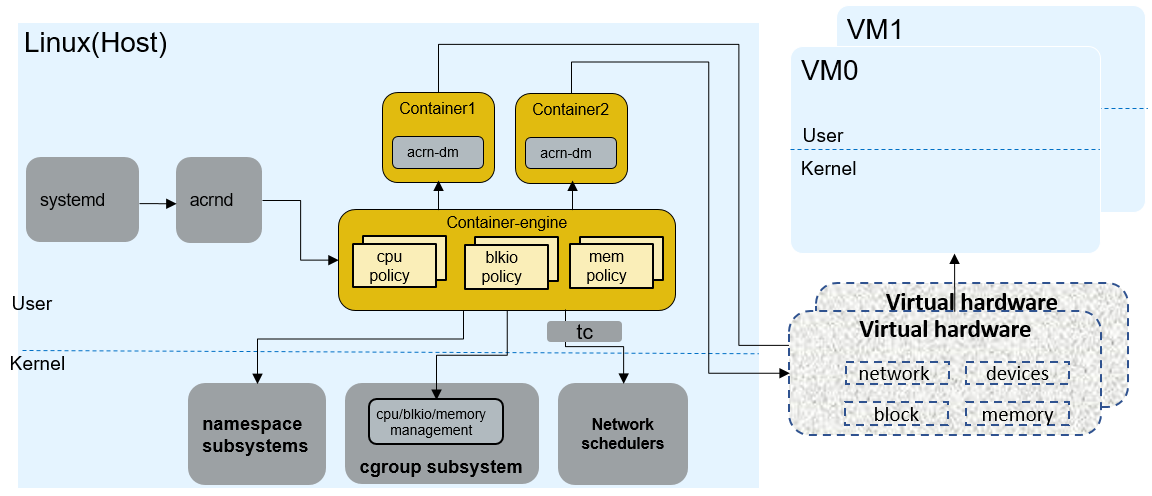
Figure 68 ACRN-DM QoS architecture
ACRN-QoS CPU utilization example¶
In runC config.json we set the CPU resource as shown below for VM0 and VM1:
"cpu": {
"shares": 1024,
"quota": 1000000,
"period": 500000,
"realtimeRuntime": 950000,
"realtimePeriod": 1000000,
"mems": "0-7"
},
In this example the cpu.shares
value is 1024, so the VM0 and VM1 device model
CPU utilization is 1024 / (1024 + 1024 + 1024) = 33%, which means
the maximal CPU resource for the VM0 or VM1 is 33% of the entire CPU resource.
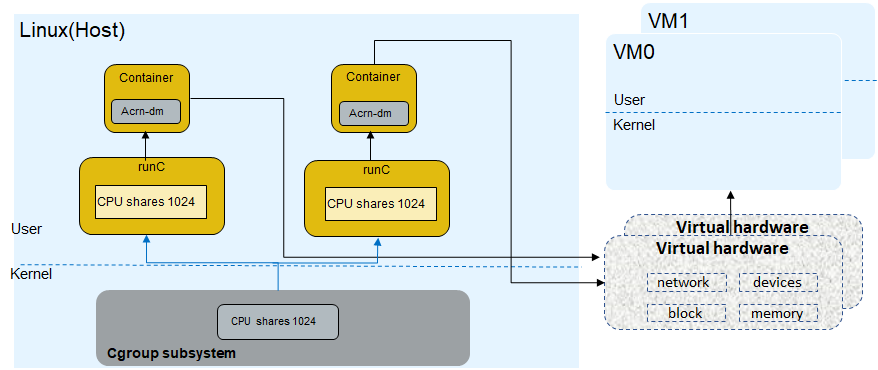
Figure 69 CPU utilization image
How to use ACRN-DM QoS¶
Follow Use SDC Mode on the NUC to boot “The ACRN Service OS” based on Clear Linux 29970 (ACRN tag v1.1).
Add these parameters to the
runC.jsonfile:# vim /usr/share/acrn/samples/nuc/runC.json
"linux": { "resources": { "memory": { "limit": 536870912, "reservation": 536870912, "swap": 536870912, "kernel": -1, "kernelTCP": -1, "swappiness": 0, "disableOOMKiller": false }, "cpu": { "shares": 1024, "quota": 1000000, "period": 500000, "mems": "0-7" }, "devices": [ { "allow": true, "access": "rwm" } ] },Note
For configuration details, refer to the Open Containers configuration documentation.
Add the User VM by
acrnctl addcommand:# acrnctl add launch_uos.sh -C
Note
You can download an example launch_uos.sh script that supports the
-C(run_containerfunction) option.Start the User VM by
acrnd# acrnd -t
After User VM boots, you may use
runc listcommand to check the container status in Service VM:# runc list ID PID STATUS BUNDLE CREATED OWNER vm1 1686 running /usr/share/acrn/conf/add/runc/vm1 2019-06-27T08:16:40.9039293Z #0