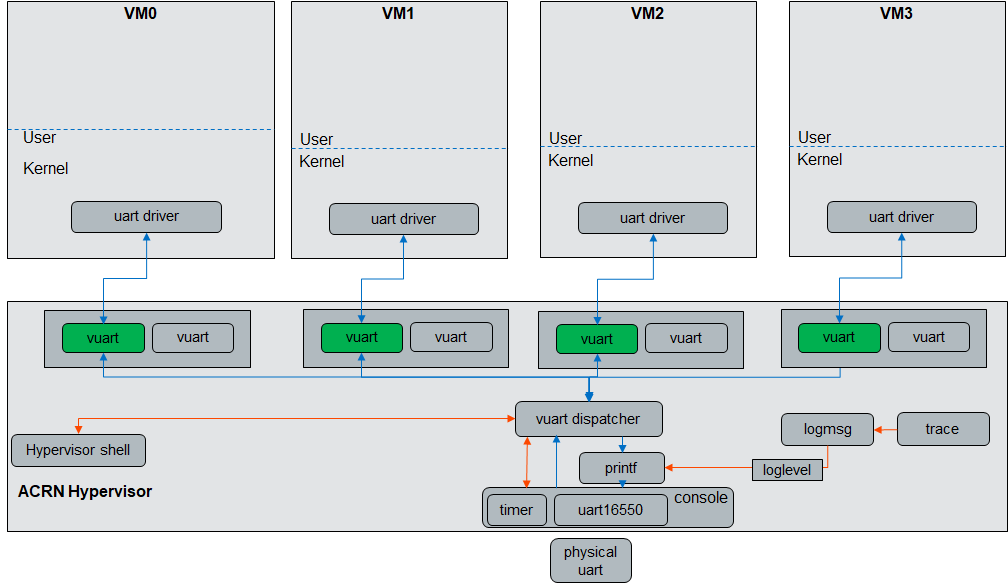
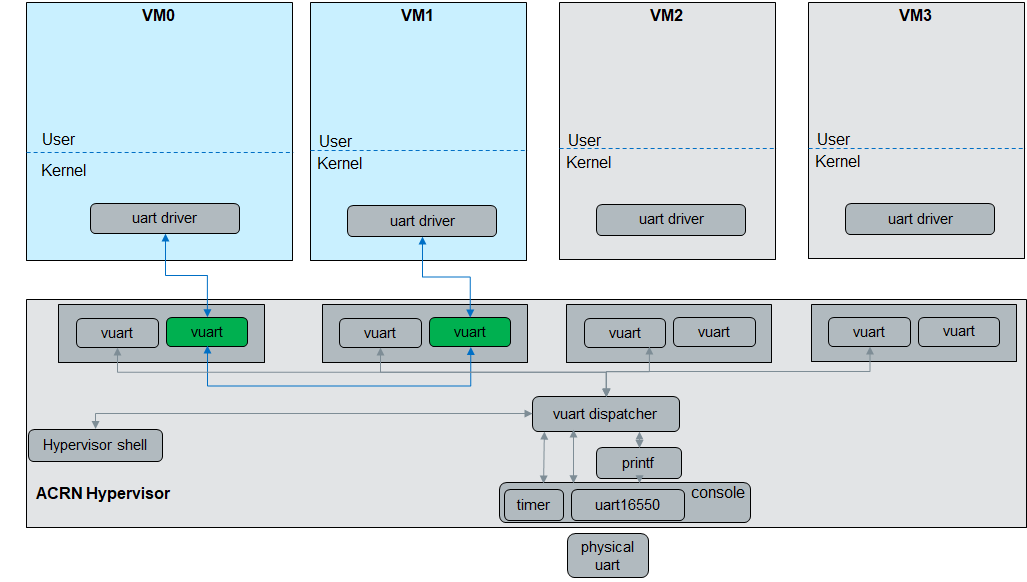
vUART Configuration¶
Introduction¶
The virtual universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter (vUART) supports two functions: one is the console, the other is communication. vUART only works on a single function.
Currently, only two vUART configurations are added to the hypervisor/scenarios/<xxx>/vm_configuration.c file, but you can change the value in it.
.vuart[0] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = INVALID_COM_BASE,
},
.vuart[1] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = INVALID_COM_BASE,
}
vuart[0] is initiated as the console port.
vuart[1] is initiated as a communication port.
Console enable list¶
| Scenarios | vm0 | vm1 | vm2 | vm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDC | SOS (vuart enable) | Post-launched | Post-launched | |
| SDC2 | SOS (vuart enable) | Post-launched | Post-launched | |
| Hybrid | Pre-launched (Zephyr) (vuart enable) | SOS (vuart enable) | Post-launched | |
| Industry | SOS (vuart enable) | Post-launched | Post-launched (vuart enable) | Post-launched |
| Logic_partition | Pre-launched (vuart enable) | Pre-launched RTVM (vuart enable) | Post-launched RTVM |
How to configure a console port¶
To enable the console port for a VM, change only the port_base and irq. If the irq number is already in use in your system (cat /proc/interrupt), choose another irq number. If you set the .irq =0, the vuart will work in polling mode.
- COM1_BASE (0x3F8) + COM1_IRQ(4)
- COM2_BASE (0x2F8) + COM2_IRQ(3)
- COM3_BASE (0x3E8) + COM3_IRQ(6)
- COM4_BASE (0x2E8) + COM4_IRQ(7)
Example:
.vuart[0] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM1_BASE,
.irq = COM1_IRQ,
},
How to configure a communication port¶
To enable the communication port, configure vuart[1] in the two VMs that want to communicate.
The port_base and irq should differ from the vuart[0] in the same VM.
t_vuart.vm_id is the target VM’s vm_id, start from 0. (0 means VM0)
t_vuart.vuart_id is the target vuart index in the target VM. start from 1. (1 means vuart[1])
Example:
/* VM0 */
...
/* VM1 */
.vuart[1] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM2_BASE,
.irq = COM2_IRQ,
.t_vuart.vm_id = 2U,
.t_vuart.vuart_id = 1U,
},
...
/* VM2 */
.vuart[1] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM2_BASE,
.irq = COM2_IRQ,
.t_vuart.vm_id = 1U,
.t_vuart.vuart_id = 1U,
},
Communication vUART enable list¶
| Scenarios | vm0 | vm1 | vm2 | vm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDC | SOS | Post-launched | Post-launched | |
| SDC2 | SOS | Post-launched | Post-launched | Post-launched |
| Hybrid | Pre-launched (Zephyr) (vuart enable COM2) | SOS (vuart enable COM2) | Post-launched | |
| Industry | SOS (vuart enable COM2) | Post-launched | Post-launched RTVM (vuart enable COM2) | Post-launched |
| Logic_partition | Pre-launched | Pre-launched RTVM |
Launch script¶
- -s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio
This option is only needed for WaaG and VxWorks (and also when using OVMF). They depend on the ACPI table, and only
acrn-dmcan provide the ACPI table for UART. - -B ” ….,console=ttyS0, …” Add this to the kernel-based system.
Test the communication port¶
After you have configured the communication port in hypervisor, you can access the corresponding port. For example, in Clear Linux:
With
echoandcatOn VM1:
# cat /dev/ttyS1On VM2:
# echo "test test" > /dev/ttyS1you can find the message from VM1
/dev/ttyS1.If you are not sure which port is the communication port, you can run
dmesg | grep ttySunder the Linux shell to check the base address. If it matches what you have set in thevm_configuration.cfile, it is the correct port.With minicom
Run
minicom -D /dev/ttyS1on both VM1 and VM2 and entertestin VM1’s minicom. The message should appear in VM2’s minicom. Disable flow control in minicom.Limitations
- The msg cannot be longer than 256 bytes.
- This cannot be used to transfer files because flow control is not supported so data may be lost.
COM port configurations for Post-Launched VMs¶
For a post-launched VM, the acrn-dm cmdline also provides a COM port configuration:
-s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio
This adds com1 (0x3f8) and com2 (0x2f8) modules in the Guest VM, including the ACPI info for these two ports.
Data Flow 1:
When the post-launched VM is started with the vUART enabled in the hypervisor configuration file only, the data flow is shown as below:
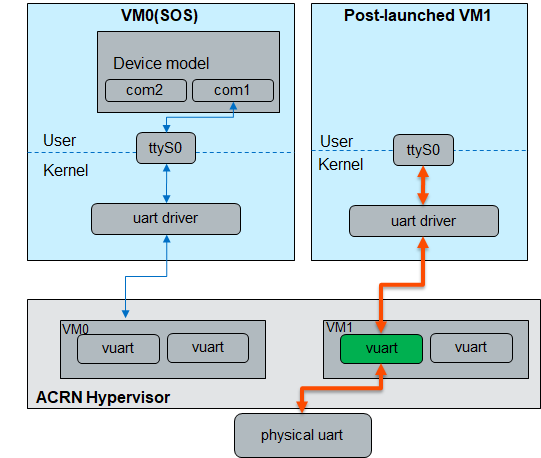
acrn-dm cmdline: N/A
vm_configuration.c: .vuart[0] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM1_BASE,
.irq = COM1_IRQ,
},
Data Flow 2:
When the post-launched VM is started with the acrn-dm cmdline of -s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio only, the data flow is shown as below:
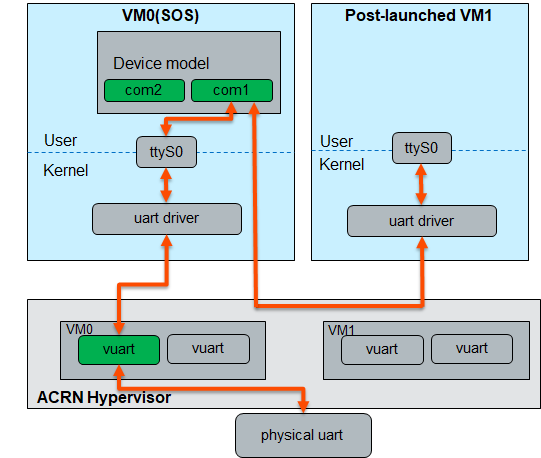
acrn-dm cmdline: -s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio
vm_configuration.c: .vuart[0] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = INVALID_COM_BASE,
},
Date Flow 3:
When the post-launched VM is started with both vUART enabled and the acrn-dm cmdline of -s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio, the data flow is show as below:
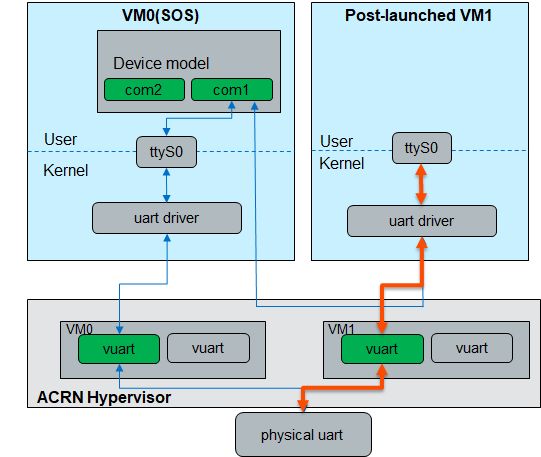
acrn-dm cmdline: -s 1:0,lpc -l com1,stdio
vm_configuration.c: .vuart[0] = {
.type = VUART_LEGACY_PIO,
.addr.port_base = COM1_BASE,
.irq = COM1_IRQ,
},
Note
For operating systems such as VxWorks and Windows that depend on the ACPI table to probe the uart driver, adding the vuart configuration in the hypervisor is not sufficient. Currently, we recommend that you use the configuration in Data Flow 3. This may be refined in the future.